With a continuously expanding wearable technology ecosystem and gradually increasing customer demand, the wearable market is now in a position to keep on advancing, offering not only modern devices but also highly-functional wearable apps to customers.
Until recently, wearables belonged to the group of devices used exclusively by military forces, businesses, and healthcare professionals. However, now, many years after the first smart wearable device was introduced, they are finally moving from a high-tech niche category to the private consumer market.
From tracking fitness activity to boosting gaming experiences – wearables have the potential to become a substantial part of consumer tech in the not-so-distant future. In this article, we are going to do a deep dive into the ins and outs of wearable technology, from what wearable is and why we need it to the benefits and challenges of wearable app development in different industries.
What is wearable technology?
Wearables, or wearable technology, are devices that can, as the name suggests, be worn on the body as accessories, implanted straight into the user’s body, or embedded in their clothing as part of the textiles and technology fusion. Today’s most popular wearable devices are smartwatches, fitness trackers, and smart glasses (one of the head-mounted display categories.)
According to Statista, in the period between 2016 and 2019, the number of wearable connected devices more than doubled, increasing from 325 to 722 million. Moreover, it is expected to grow to surpass one billion by 2022, in no small part due to the global 4G to 5G evolution that is already ongoing in the telecom industry.
One of the key characteristics of wearables is that they normally make hundreds of thousands of measurements per day. The user’s personal data is monitored and measured upon their consent through powerful smart sensors and microchips embedded in a wearable electronic device. For this very reason, the development of this technology is closely associated with the growth of mobile networks, high-speed data transfer, and miniaturized microprocessors. Besides, it is common knowledge that the connection to Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or cellular networks only further enhances the user experience for wearables.
In addition to tracking biometric data, wearables can also access applications and provide feedback based on the processed information. This way, wearable technology in many respects follows in the footsteps of the Internet of Things. Just like in the case with wearables, it also took IoT some time to enter the private sector, but once it did, the popularity immediately started to increase. Furthermore, wearable devices not only follow the example of their big brother but also are actually evolving into a major category of the Internet of Things, with its numerous life-changing applications. What differentiates wearables from IoT is that a corresponding wearable app should work independently of a phone app. It generally gives users greater flexibility. Yet, if done reasonably, it is still an option to share the load between a wearable app and a companion phone app.
Why do we need wearable technology?
The revolution began a couple of years ago when the Apple Watch was introduced, and the watch per se – an accessory telling time – overnight turned into a smart device that was pretty good at many other more technically challenging tasks. Since then, ongoing demand has been continuously fueling a strong growth trajectory for wearable devices.
Yet, the question remains: Why should we care about wearables and wearable apps?
The short answer is they can make our daily lives easier. Whether a wearable device is worn on the body or incorporated into the clothes, its purpose is the same, which is to provide permanent, portable, convenient, and in some instances, hands-free access to computers. This access, in turn, can bring about the following benefits to people:
Wearables help us track data better and thus contribute to maintaining and improving our health.
They can make many tasks less of a hassle to complete – be it contactless payment, navigation in the surroundings, or responding to text messages.
Wearable technology has the potential to improve lives by encouraging proactive healthcare and active living.
Wearable technology is equally suitable for work and life. It can help improve productivity at the workplace or be part of devices meant for entertainment.
Wearables have the social aspect that allows for gamification of personal achievements tracking and sharing – be it a workout completion, recovering from a condition, or success in reducing and quitting smoking.
Benefits of wearables for different industries
Smartwatches and other wearable devices do not seem to stop gaining in popularity. Yet, to ride this wave, one has to know where to find it in the first place. Today, there are three big industries that one has to consider when looking into the ways to become part of the global wearable tech market: healthcare, gaming, and fashion.
1. Wearable devices in healthcare
In 2022, healthcare is a big deal, and in part, therefore, the healthcare industry continues welcoming tech innovations to better safeguard people and improve the delivery of care.
Wireless medical sensors are not entirely new to the health industry. In fact, there are several ways in which sensors have been used in healthcare for years. From body measurements to the quality of sleep, from heart rates to respiratory functions and beyond – the sensors are nearly everywhere. They communicate with each other creating an ecosystem that stores all health-related data about a person. As a result, individuals and their healthcare providers get empowered to monitor their health 24/7 and manage their medical conditions more seamlessly. However, as wearable technology is becoming more integrated into the average customer’s life, there is no need for wearable apps to be directly connected to medical staff. It is likely that such applications will respond to the retrieved and analyzed data with alerts or suggested actions anyway. Receiving feedback, awards, and reminders about one’s health and fitness goals can be satisfying enough.
This promise of complete awareness is a huge part of why the number of people using wearables for health reasons is forecast to steadily grow. Thus, yet in 2018, Accenture conducted a study on digital health services, revealing that 33% of respondents had adopted wearables – compared to 9% in 2014 – and what is more exciting is that 72% of consumers said they would agree to share personal data collected from their wearable devices with their insurance carrier.
Wearable devices used in preventative care, diagnosis, treatment decision-making, and even high-risk care management were estimated to save over $200 billion across all conditions in the US by 2050. Moreover, according to recent research from Insider Intelligence, the number of smart wearable users in the US will reach 72.6 million.
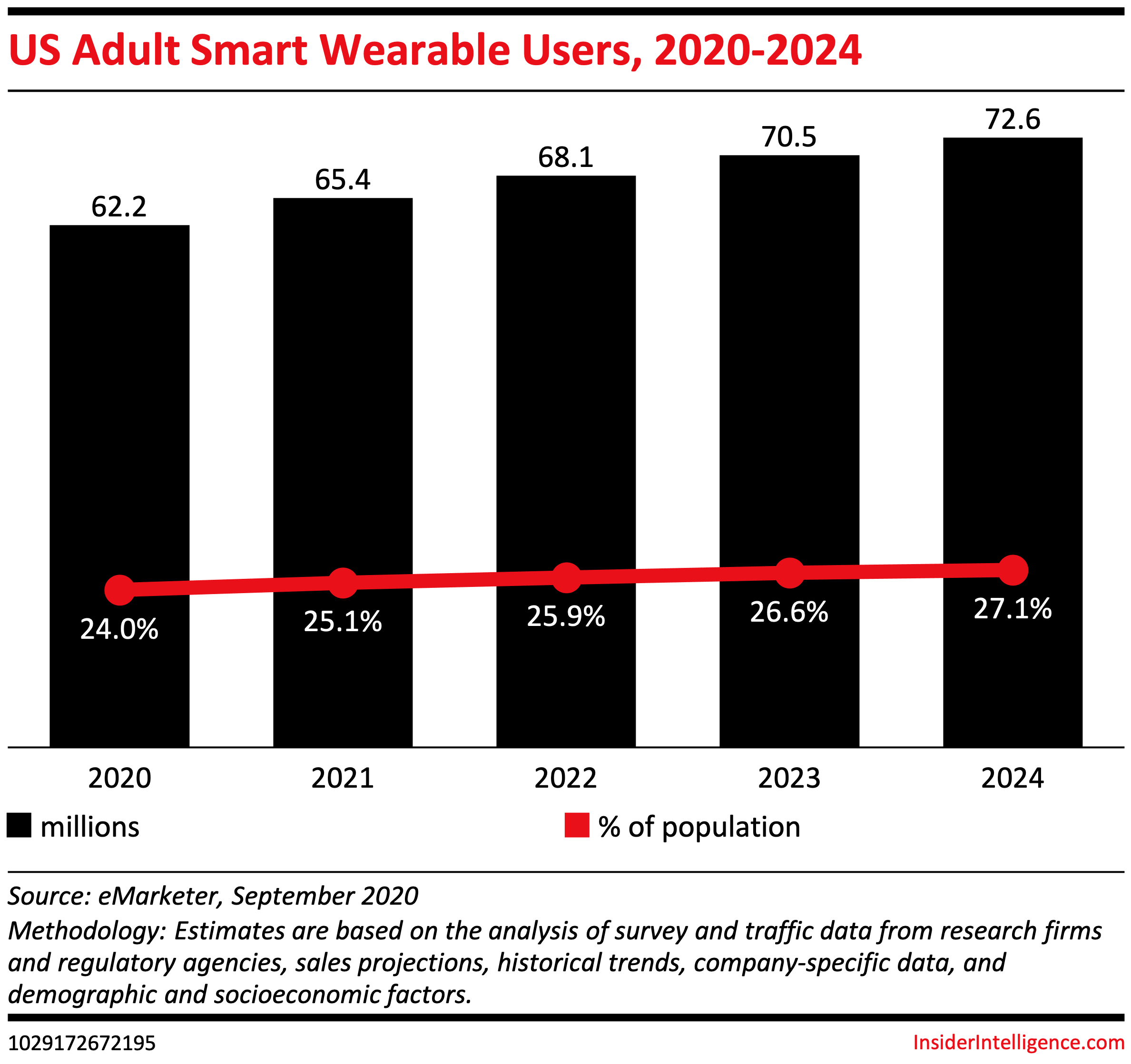
With the ability to track fitness activity, evaluate sleep quality, and measure health data like heart rate or blood oxygen level, wearable devices continue becoming more and more advanced. Today, there are so many things besides step tracking. Similarly, the selection of wearable devices for health monitoring is only widening:
Wearable fitness trackers - fitness-tracking smart bands (Fitbit, Jawbone, Runtastic, Garmin, etc.) and smart rings (Oura, Oumij, Motiv, etc.)
Smart health watches - smartwatches running Wear OS, Galaxy Watches from Samsung, and Apple Watches from Apple.
Body-mounted sensors - a variety of sensors monitoring biological data for healthcare purposes:
- Wearable ECG monitors
- Wearable blood pressure monitors
- Biosensors detecting pulse rate, blood oxygen and glucose levels, muscle oxygen saturation, and more
Although fitness trackers were the first wearable devices to become particularly popular among the broad audience, smartwatches have followed the lead. As a result, they managed to grow into a massively popular staple of the consumer electronics industry and a fixture of the watch industry's middle market.
Another important component of smart wearable devices used for healthcare purposes is algorithms. Wearable devices powered with an algorithm could alert users when any irregularities in their biological data are detected whether these symptoms signal a specific medical condition’s presence. Algorithms in wearables are the next-gen development that is being extensively studied today. So, the usage of smart wearables to determine symptoms of a particular infection, for instance, is not science fiction but rather an eagerly anticipated feature.
2. Wearable gaming technology
Gaming and technology are inseparable. Moreover, since customer expectations tend to quickly align to new developments in the game design field, the need to continue to grow and achieve more is always there when it comes to game development.
Wearable gaming technologies are exactly one of those developments that have been gaining a lot of attention in recent years. They are not a new thing, and in 2022, they will continue to grow. It all began decades ago with the first prototypes of modern VR headsets. Today, Virtual Reality wearable devices remain one of the most common forms of wearable technology in the gaming industry. Yet, as it was mentioned, customers want their gaming experiences to be better with each new release, so wearable haptic devices are a perfect candidate for the job.
VR wearables. Virtual reality headsets were the first type of wearables used in gaming. VR gaming headsets and goggles help users immerse themselves entirely in the game. That is why up until now, the most important VR gaming accessory is the one users wear on their heads. The selection of these wearable VR gaming devices is wide enough to fit any budget: from simple VR goggles displaying the simulated 3D game environment to advanced motion-control VR headsets capable of capturing and transmitting full user’s head and eye movements.
Haptic devices. Another dimension of involvement that wearables can provide in gaming is tactile feedback. In games, touch is engaged through the science of haptics. Video game controllers have been using haptics for nearly two decades already, but incorporating this technology into wearable devices is the next achievable milestone.
Thanks to the recent advancements, gamers can now use wearable devices that provide haptic feedback to the body. Haptic vests, gloves, or suits can make gaming more realistic. Haptic actuators are ultra-thin and small, which enables more exciting interactions with technology and new vivid tactile sensations. The technology is evolving, and therefore, we should look forward to haptics becoming more useful across a wide variety of gaming wearable devices.
3. Wearables in fashion
The fashion industry is just as perceptive to original ideas and innovation as the gaming sector is. Trends come and go, so when anything exciting looms on the horizon, it cannot but be picked up to become somebody’s fashion statement.
Wearable smart devices have taken over the fashion industry and do not seem to move over. Smart garments and accessories are now part of intelligent fashion that combines aesthetics and style with functional technology. There are already quite a number of ways in which wearables are used in the fashion industry. For instance, your smart accessories can change color to match any of your outfits, your smart bag can charge your phone or other USB devices, and your purse can turn on internal lights every time you open it.
Moreover, there is even such thing as smart fabrics that are being increasingly used by famous brands like Levi’s. Their smart apparels are designed to have sensors measuring biometrics. This way, suits, pants, and other clothing accessories turn into wearable devices whose unique fabric can adjust the temperature or even enhance blood flow.
Wearable apps are rapidly taking over the fashion industry. According to the report by Statista, the global smart clothing and fabrics market size is estimated to substantially grow from 2018 to 2025. Estimates compiled from multiple sources have it that in 2025, the smart clothing and fabrics market will reach the size of over 5 billion U.S. dollars.
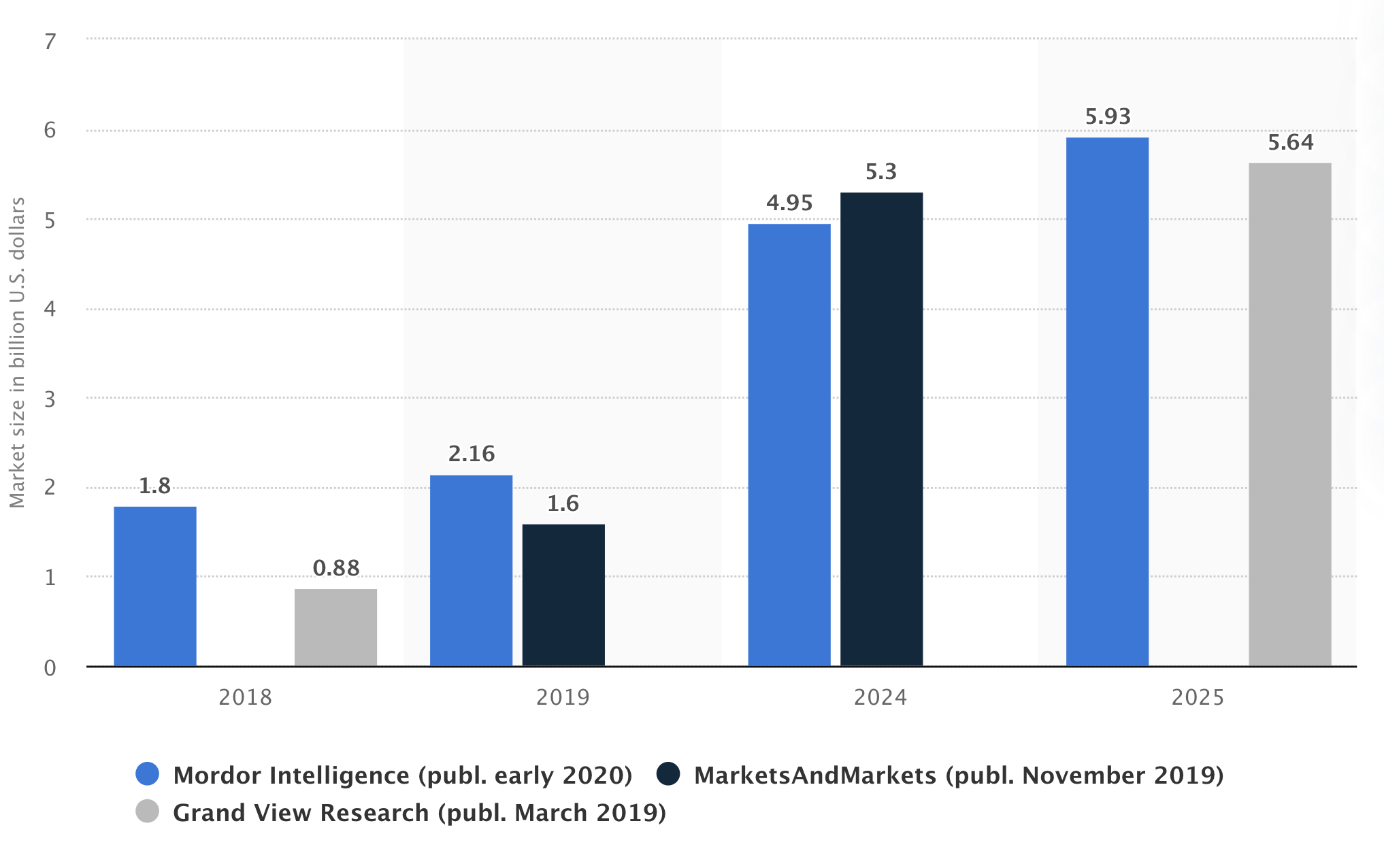
Challenges in wearable app development
One way or the other, every coin has two sides. Similarly, there is no cutting-edge technology that wouldn’t have some challenges to be handled. The wearable devices market is no exception. Let’s take a look at the most nagging problems that are likely to arise when you decide to develop a wearable app.
1. Battery issues
Thinking about ways to expand a wearable device’s battery life is a must for anyone in the wearable business. Wearable devices are normally small and lightweight, so no wonder why battery life has always been such a big issue. So, it is critical for wearable device vendors to design an efficient, high-performing, and long-lasting battery. Yet, wearable app providers have to keep this particularity in mind as well when developing their products.
The market is already highly competitive, and the wearable app that consumes too much battery is not likely to survive. The wearable device software – portable by its nature and nearly always connected to the internet – does not have to make a user recharge the device too often. At the same time, however, this app must be capable of balancing between useful functionality and battery-saving features.
2. User interface
A wearable app should both function smoothly without draining a battery and look attractive on wearable devices. The biggest challenge here is that normally, wearable devices have much smaller screens than smartphones. Therefore, the user interface of a wearable app must be designed with a set of basic rules in mind:
- Remove visual clutter in the UI to allow for its glanceability
- The UX/UI has to convey messages properly, so make a UI clear and minimalistic
- The displayed content must be relevant to the user context
- The content should be displayed against a light enough background
- Design singular focused tasks that create an efficient flow
- Make notifications unintrusive and valuable for a user
- User sessions on wearables are short, so interactions must be as lightweight as possible
3. Privacy and security
Any app provider – regardless of the vertical or the level of sophistication – must always opt for more privacy and security for its users.
First of all, wearables are designed to be continuously connected to the internet and support data transfer from one device to the other. It is beneficial for the user experience but is also associated with the increased risk of data breaches. That said, it is the app provider’s responsibility to eliminate the risk and prevent data robbery by third parties.
On top of that, wearable devices’ displays can easily become the source of the data leak, too. A good practice is to make content on a wearable device’s screen glanceable. As a result, if designed poorly, users’ sensitive health data or private conversations can be visible on a wearable device when it is in plain sight. However, there are ways to overcome this problem by efficiently designing wearable UIs. Thus, one has to consider which way the wearable is facing and, based on that, decide how information should be displayed. As a rule of thumb, the screen should remain blank when it is not safe to do otherwise, and whenever a notification arrives, the device must vibrate first and only then display this notification. One way or the other, respect your customers and always aim to help them protect their data!

4. Functionality
An attractive, minimalistic, and easy-to-navigate interface is an integral part of what a great wearable device should be like. Yet, one should never sacrifice functionality for aesthetic reasons.
In fact, the more useful functionality a wearable device offers, the better. To attract and retain users, wearables should prove that they are here for a reason and that they can actually achieve what would not otherwise be possible. A wearable app must enable features that would add brand-new benefits. For instance, a sleep-tracking wearable app should not just tell how long you slept or how often you moved at night, but instead, it should suggest advice on improving the quality of sleep based on your sleeping habits. A wearable app’s functionality must rely on personalization and customization not achievable on other devices to be justified.
5. Regular updates
There could hardly be a moment for an app when all its users will get completely satisfied with how it looks and works. In fact, it is much more likely that most of them will never be absolutely happy with the services of an app.
That said, any application – and a wearable app is no exception – need to be regularly updated. Only with continuous upgrades, the app will be able to remain relevant and useful. Regular updates help address quality-related issues, and new releases are the only way to deliver new features and fix bugs.
6. Multi-platform support
It is natural that with wearables, boundaries between devices have begun blurring. Ideally, wearable apps should be compatible with multiple platforms. Yet, this device fragmentation, in turn, started to hinder multi-platform app development.
Therefore, in reality, it is rarely possible to make a wearable app that would run seamlessly on different devices. Wearables are often tied to proprietary platforms, and third-party app development is very limited, if not impossible. For instance, some vendors manufacture devices so that their OS would not be modifiable. Thus, to run on multiple platforms, a wearable app must rely on a genuinely vendor-independent platform.
Nevertheless, many wearables are usually paired with a smartphone. They rely on the respective smartphone companion app to benefit from internet connectivity and for better performance. It further complicates the situation as cross-platform development approaches must support each combination of host and watch platform. This leads us to the next and last challenge that wearable app developers can encounter.
7. Tethered devices
Interaction with other devices is essential for wearables. Their limited functionality and generally much smaller screens are some of the reasons why wearables are tethered – connected – rather than standalone devices. Wearables rely on larger devices when trying to live up to the performance standard. This tethering unlocks access to more features, but there is also a reverse side to it.
If the battery of that larger device – a smartphone, tablet, etc. – has run down, the wearable itself becomes useless.
If the device that a wearable is connected to is beyond the Bluetooth connection range, operations get much less smooth or stop altogether.
An app that is managed by two devices has twice as many reasons to fail.
Accordingly, developers should not think of wearables in isolation when designing apps for them. Until there is a rock-solid solution that would enable wearable devices to function flawlessly on their own, it is nearly compulsory to integrate them with the existing devices in a user’s digital ecosystem. Moreover, this must be done so that all the connected devices can benefit from each other, thus providing the user with the best possible outcomes. For instance, a smartwatch that measures heart rate and blood oxygen and a smartphone that provides the in-depth analysis of the collected data are great examples of effective cooperation between a wearable and companion app.
Conclusion
Wearable technology is strong and growing. Today, it has everything to achieve success in the future and let those who create wearable devices and software for these devices finally hit the big time.
Wearable technology’s benefits are multifold, but the related challenges are equally significant. Still, by most accounts, the former is expected to overweigh the latter, as the businesses see the bright prospect for wearables and are willing to help others see that coming. With the right combination of hardware and software, wearables will definitely manage to serve the purpose of improving people’s lives.
If you have a wearable app idea or want to learn more about present possibilities for wearable app development, reach out to us using the contact form below! Our consultants will do their best to put to good use their tech expertise and experience developing wearable applications.

© 2022, Vilmate LLC




