In the relentless march of technological progress, the evolution of wireless communication has been nothing short of remarkable. The evolution from early mobile telephony through the advent of 5G's immense capabilities has completely transformed our way of connecting, communicating, and experiencing the world.
This journey through different generations of mobile networks represents speed improvements and major changes in industries, global economies, and daily life.
Today, our discussion revolves around the critical significance of reliable wireless connectivity. We will delve into the distinctions among 3G, 4G, and 5G while also contemplating the prospective landscape of wireless communication.
Brief overview of the fundamentals
First, clarify that the “G” title stands for “Generation.” Presently, we recognize five generations of wireless networks. The first and second mobile communication generations are scarcely remembered nowadays. They have become wholly obsolete and are no longer in use. Nonetheless, we will still discuss them in the context of history.
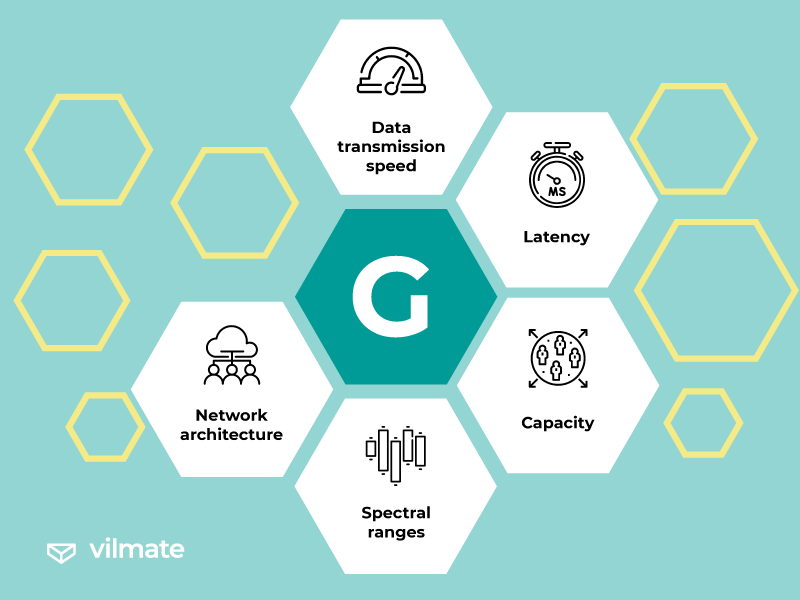
We need to understand the comparative criteria and features to comprehend the disparities between 3G, 4G, and 5G. We must consider five essential characteristics:
- Data transmission speed: Each generation primarily aims to improve data transmission speed, which remains a crucial criterion.
- Latency: Latency gauges the delay between sending and receiving data.
- Capacity: This parameter determines the ability to handle a specific number of devices. Each successive generation can support significantly more devices than its predecessor, facilitating the consistent growth of the Internet of Things.
- Spectral ranges: Different generations utilize distinct frequency ranges for communication. For instance, 5G employs a broader spectrum, including high-frequency millimeter wave ranges for ultra-high speeds and a mid-range for balancing between speed and coverage.
- Network architecture: This criterion enables the network to be divided into segments, each with its own objectives.
Let’s delve more comprehensively into the progression of advancements and explore why the shift from the 3rd generation to the 4th transpired and how the 4th generation laid the foundation for the development of 5G.
The evolution of Mobile Wireless Communication
Before 1973, mobile communication literally moved on wheels. Users installed telephones in their cars and other vehicles, enabling them to carry the devices wherever they went. The emergence of the first portable mobile phone can be attributed to Martin Cooper, the executive director of Motorola. Under the guidance of company leader John Mitchell, this groundbreaking development played a pivotal role in propelling the company to the forefront of mobile communication innovation.
1G and 2G
The Initial phase of mobile communication was analog and hadn’t yet been termed a “Generation.” This wireless communication was predominantly utilized in car phones. While the technology was relatively sluggish and lacked anti-fraud measures, it still managed to captivate the interest of thousands of users.
The progression to the Second generation of phone systems commenced in the 1990s and marked a shift towards digitalization. Two primary standards emerged as major contenders in the global market: the European GSM and the American CDMA.
The 2G era introduced off-channel communication between mobile phones, enabling SMS messaging and granting access to multimedia content. Notably, in 1998, Finland and Sweden pioneered using mobile phones for payments, allowing users to purchase from Coca-Cola vending machines and pay for parking spaces.
The surge in user interest in the 2G network was nothing short of explosive, prompting companies to vigorously advance mobile technologies and inch closer to the eventual invention of the smartphone. Over time, the 2G network metamorphosed into 2.5G and even 2.75G iterations. However, the escalating user demand ultimately underscored the necessity for a new, refined technological paradigm.
Wireless Mobile Communication: The era of 3G
Mobile phone usage had become widespread, and the demand for data was on the rise. Consequently, companies faced the challenge of providing people with access to wireless mobile Internet. The primary focus remained on enhancing data transmission speed. The capabilities of 2G technology were proving limiting, prompting the industry to embark on developing the next generation.
Unlike its predecessor, 3G technology embraced packet-switching for data transmission, departing from the earlier circuit-switching approach. During the creation of the third-generation network, developers set their sights on specific speed benchmarks: 2 Mbps indoors and 384 kbps outdoors.
The remarkable connection speed of 3G heralded a true technological revolution, fundamentally transforming the landscape of data transmission. For the first time, companies could deliver radio content and television programming directly to mobile phones. It was companies like RealNetworks and Disney that first harnessed these innovative capabilities.
The Mid-2000s marked a pivotal phase in the evolution of the third generation of mobile networks. This era saw the emergence of High-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) technology, effectively elevating 3G to its enhanced iteration known as 3G+. This upgrade brought forth accelerated data speeds and heightened transmission capacities, reaching an impressive 14 Mbps.
By the end of 2007, an estimated 300 million subscribers were actively engaged with 3G networks. This technological stride generated substantial revenues in the same year, surpassing 120 billion dollars. The majority of mobile phones introduced post-2007 seamlessly incorporated robust 3G connectivity. Notably, Apple even integrated this technology into the nomenclature of its second-generation smartphone, aptly naming it the iPhone 3G.
Mobile phones had prior internet access, but it was only after 2007 that users embraced a new dimension of data transmission speeds. This technology found an extended demand, even reaching laptops, which led to the emergence of specialized devices and routers facilitating computer connectivity to mobile wireless networks. As market demands flourished, introducing “netbooks”, laptops accommodating SIM cards for network access, became inevitable.
By 2010, wireless internet integration had expanded its reach to encompass electronic books, notably the Amazon Kindle, while Apple also embraced this innovation within its iPads.
Consequently, the proliferation of devices and users burgeoned. It became evident that it was essential to develop a fresh technology capable of managing the mounting demand for bandwidth-intensive applications. The advent of 4G technology became an anticipated inevitability.
4G IP Networks
As early as 2008, the International Telecommunication Union-Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R) had already established requirements for the forthcoming generation of technology. The service speed for 4G was envisaged to reach 1000 Mbps for high mobility communication and 1 Gbps for low mobility scenarios. Nonetheless, at that juncture, achieving such speeds remained beyond reach.
The initial iterations of 4G were WiMAX and LTE. Despite not initially meeting the stipulated speed criteria, they were frequently marketed as 4G solutions by providers. This situation culminated in the ITU-R subsequently revising its criteria. By 2010, any technology surpassing 3G speeds was classified as fourth generation.
Diverging from its predecessors, the fourth generation relies on IP protocols, thereby enabling the conveyance of high bit rates. Contemporary 4G boasts download speeds of up to 150 Mbps, marking a substantial leap from the capabilities of 3G (up to 7 Mbps).
As of 2021, 4G technology had permeated 58% of the global mobile technology market. However, progress is an unwavering force, propelling us toward the proliferation of novel technology.
5G Cellular Mobile Communication
The journey towards the fifth generation of mobile technology began in 2008, with NASA and Jeff Brown at the helm of its initial development. Four years later, New York University established a dedicated research center to delve into the potential of 5G technology. The paramount objective of these researchers was to engineer a mobile standard that could deliver higher speeds while simultaneously optimizing energy efficiency and the allocation of the radio frequency spectrum.
In 2013, Samsung Electronics made a significant revelation, declaring the successful creation of a 5G technology capable of delivering speeds in the range of tens of gigabits per second. Rigorous tests underscored the remarkable capabilities of this emerging mobile network generation, showcasing data transmission speeds of 1.056 Gbps across distances of up to 2 kilometers, leveraging an 8x8 MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) configuration. The employment of MIMO technology, encompassing multiple transmitting and receiving antennas, dramatically amplified the channel’s throughput capacity.
The introduction of 5G technology followed a traditional trajectory, with its initial rollout by providers in Japan in 2013. However, South Korea spearheaded the full-scale adoption of this innovative technology in 2019. Subsequently, the United States and the Philippines joined the vanguard of 5G adoption alongside Korea.
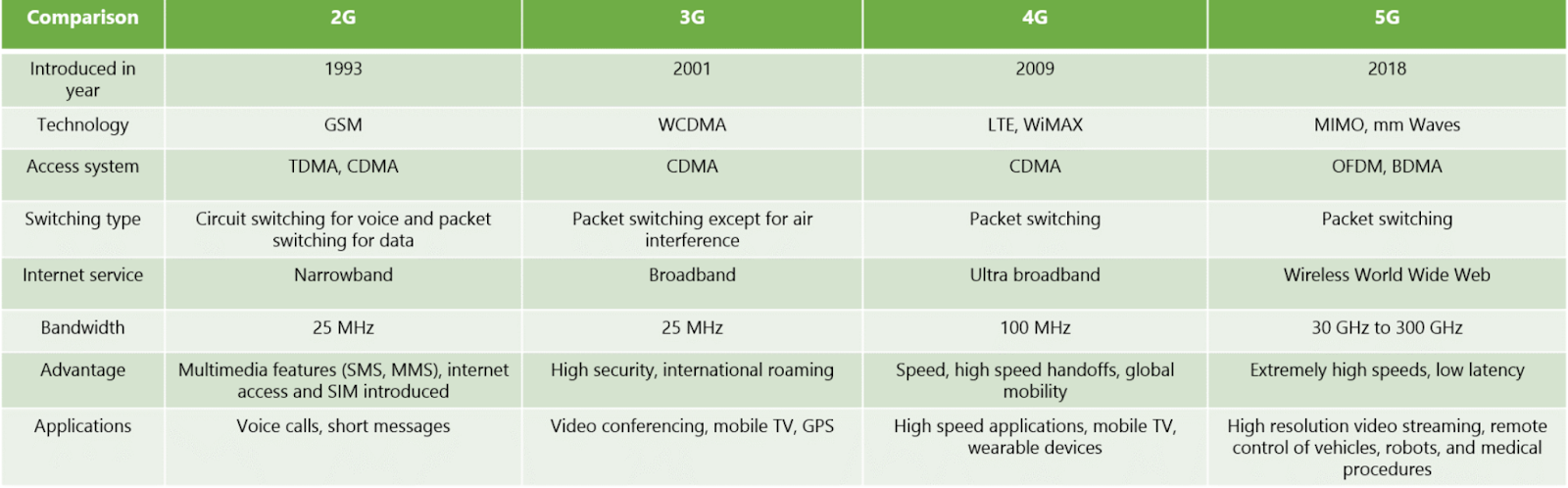
A diverse range of devices seamlessly incorporate 5G technology in the present landscape, underscoring the global preparedness for this transformative phase. In light of this, we present a comparative table outlining the evolution from 2G through 3G and 4G, culminating in 5G technology, providing a vivid illustration of the progression across generations.
Nonetheless, despite the manifold advantages and potential offered by 5G, the technology isn’t exempt from vigorous discussions - a topic we will delve into further.
Why is there fear surrounding 5G?
The advent of 5G promises to enhance our lives with unprecedented comfort and propel the Internet of Things into a new development realm. Debates regarding the fifth-generation networks persist, encompassing a lot of concerns:
- Health and safety: Concerns are raised over the potential impact of high-frequency radio waves on human well-being. However, a wealth of scientific research consistently underscores that stringent safety standards governing 5G and other wireless technologies are adhered to, effectively dispelling significant societal threats.
- Environmental considerations: Apprehensions revolve around the ecological implications tied to the expansion of 5G infrastructure, encompassing the installation of novel towers and equipment. Such impacts necessitate a more profound examination to ensure the sustainable evolution of this technology.
- Infrastructure and land utilization: The rollout of 5G entails a heightened need for tower and equipment installation, which can spark discussions concerning land resource allocation and the utilization of public spaces.
- Competition within equipment provision: Geopolitical dynamics may spark discourse surrounding the selection of equipment suppliers for 5G networks. Certain countries express concerns regarding security vulnerabilities and potential dependencies on specific providers.
- Information security: The proliferation of connected devices and escalating volumes of transmitted data underscore the urgency for elevated levels of cybersecurity measures against potential cyber threats and data breaches.
- Implications for industries and employment: The introduction of 5G can catalyze transformations across diverse economic sectors, including the integration of automation and the potential reduction of jobs in select fields.
- Economic dimensions: The integration of 5G requires substantial financial investments. Contentions could arise regarding the equitable distribution of costs among governmental bodies, communication operators, and consumers.
Nonetheless, these ongoing debates will likely not impede the global expansion of high-speed mobile Internet. The manifold benefits and capabilities ushered in by 5G technology are simply too substantial to ignore.
The impact of High-Speed Connectivity on the market and business activity
Without a doubt, the Internet has become an integral component of contemporary business operations. Network disruptions incur substantial costs. According to an Open Gear study, unstable internet connections resulted in losses exceeding $1.2 million for 31% of companies.
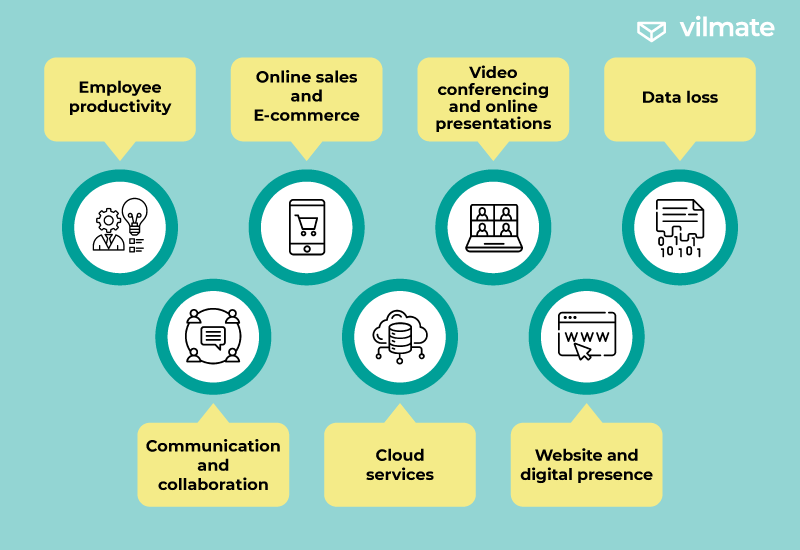
What are the repercussions of lacking a stable internet connection on revenue generation? Here are several key factors to consider:
- Employee productivity: When internet connectivity is frequently interrupted, employees encounter delays in executing tasks. Fast connection can precipitate decreased productivity levels and an extended timeframe for task completion.
- Communication and collaboration: Unstable internet connections can hinder seamless collaboration between teams, mainly when online tools are employed for data exchange and cooperative projects. Latency in data transmission may give rise to misunderstandings and communication errors.
- Online sales and E-commerce: Businesses reliant on online sales and e-commerce are susceptible to disruptions stemming from unstable internet connections. These disruptions can lead to order processing glitches, customer inaccessibility to websites, and consequential revenue loss.
- Cloud services: Many enterprises harness cloud services for data storage, project management, and assorted operations. However, unstable connectivity can impede access to these services, compromising data efficiency.
- Video conferencing and online presentations: If a company frequently conducts video conferences or delivers online presentations to clients and partners, inconsistent internet connections can negatively impact audio and video quality, tarnishing the business’s professional image.
- Website and digital presence: The recurrent unavailability of a company’s website due to unreliable internet connectivity can leave a dent in the business’s reputation and erode the trust of its customer base.
- Data loss: Unstable connectivity exposes businesses to the risk of data loss, particularly during critical transaction processing. It can culminate in financial losses and legal entanglements.
Maintaining an uninterrupted, secure, and swift connectivity fabric for businesses of all scales is paramount. Let’s delve into how this pioneering technology is poised to influence the advancement of various sectors.
5G's Transformative impact on industries
The influence of fifth-generation technology can vary across distinct domains, driven by specific underlying factors.
- Accelerated Data Transmission 5G introduces an unparalleled level of high-speed data transmission, enabling instantaneous downloads and uploads of substantial data volumes. This heightened velocity in connectivity optimizes data management, utilization of cloud services, and seamless information exchange.
- Expansion of Mobile App Capabilities The rapid speed and minimal latency characteristics of 5G redefine the boundaries for crafting mobile applications with intricate functionalities. These advantages enhance customer interactions and create fresh avenues for generating revenue.
- Elevated User Experiences The swift and stable 5G connection elevates user experiences, offering exceptional performance in streaming high-resolution videos, immersive gaming, and seamless engagement with virtual and augmented reality.
- Pioneering IoT innovations 5G’s capacity to connect an extensive array of devices to the network without compromising connection quality ignites the potential for innovative solutions, such as smart cities, Industry 4.0 initiatives, intelligent homes, and other groundbreaking IoT applications.
- Advancement of Autonomous and Self-Driving Technologies The ultra-low latency and remarkable speed of 5G play a pivotal role in advancing autonomous vehicles and self-driving technologies. This transformative technology propels progress within the transportation sector and unlocks new dimensions of opportunity.
- Unveiling Virtual and Augmented Reality Leveraging 5G connectivity, creating more immersive and realistic virtual and augmented realities becomes feasible. These immersive technologies find diverse applications, spanning from entertainment to education and even healthcare.
- Empowered Cloud Computing 5G holds the potential to amplify cloud computing capabilities and remote data processing on distant servers, significantly benefiting enterprises reliant on cloud services and resources.
Of course, the benefits of fifth-generation technology extend not only to businesses but also to everyday individuals. Thanks to 5G, users can seamlessly stream video content, engage in online gaming with minimal delays, swiftly download essential media files, manage their finances, and access telemedicine services. The revolutionary capabilities of 5G technology have empowered the transformation of our homes into “smart” environments.
With all these remarkable advantages, as of 2023, there are around 236 million active 5G subscriptions worldwide. China stands at the forefront of this technology’s adoption, closely followed by the United States. While the global transition to 5G is ongoing, the industry is already gearing up for the next phase of technological evolution. What does the future hold for us?
Anticipating 6G Technology: What to expect and when?
As we look ahead to the potential of 6G technology, we must acknowledge the immediate evolution within the 5th generation - specifically, the upcoming arrival of 5G Advanced. Set to be built upon the 3GPP’s Release 18 standard, this innovative iteration is projected to make its debut in 2024.
5G Advanced is poised to introduce enhancements that revolve around Artificial Intelligence and Extended Reality, pushing the boundaries of applications within these realms even further.
Turning our attention to the prospects of 6G, Nokia has boldly asserted that it will build upon the already established advantages of the 5th generation, taking them to unparalleled heights. Anticipated outcomes include the transformation of robotics, the advancement of smart urban infrastructure, agricultural practices, and a transformative user experience.
While experts haven’t yet outlined precise technical specifications for 6G, there is a prevailing consensus that this technology will be capable of handling unprecedented volumes of data. Theoretical data transmission speeds are projected to reach an astonishing 1 Terabit per second (Tbps), while practical data transmission will hover around 1 Gbps. Moreover, the bandwidth is poised to expand to an impressive 100 GHz, a substantial leap from the 1 GHz of 5G. Furthermore, latency is expected to be significantly reduced, dropping from 1 millisecond to just 100 microseconds (μs).
Given the historical pattern of development, which typically takes a decade per generational leap, the emergence of 6G is anticipated around 2030. Likely, this technology will first become prevalent in the Asian market, with Japan possibly taking the lead once again.
Yet, before we venture into future speculation, focusing our energy on the present landscape is prudent. The global embrace of 5G is still underway, and many enterprises must prepare for its transformative impact. Therefore, the imperative of the moment is to champion the progression of 5th-generation mobile communication while spreading awareness about its transformative advantages.
So what do we eventually have?
In closing, the trajectory of mobile network technology continues its captivating evolution, with 5G poised at the forefront of this transformative journey. Beyond delivering high-speed Internet, 5G promises to reshape the way we engage with the world around us. Its advent heralds new vistas across education, entertainment, business, and societal advancement.
The merits of 5G are manifest: rapid data transmission, minimal latency, and a steadfast, dependable connection. These attributes heighten our day-to-day experiences with mobile devices and fuel innovative technological breakthroughs and advancements.
Should you require adept guidance in harnessing the potential of 5G for your business, Vilmate stands ready to offer its capable assistance – from conceptualizing and developing cutting-edge mobile applications to ensuring secure connections. Our accomplished experts wield profound expertise and experience in information technology.




