The cloud computing industry is constantly evolving, so no wonder that the cloud stack has been a hot issue for almost a decade now. There has also been a lot of debate about its importance for businesses and the growing speed at which third-party clouds are being adopted. Then, it is to the interest of those who are willing to find their bearings and unlock the full potential of the cloud to grasp clearly and fully its nature and character. Easier said than done but still possible. This is why we would like to shine the spotlight on this phenomenon and the reasons for its being so popular. What one should do to achieve that is to break the idea down moving from an umbrella term to more concrete notions.
The cloud computing pile makes up a threefold system that comprises its lower-level elements. These components function as formalized cloud computing delivery models:
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
It is no exaggeration to say that these offerings are mapping out the future computing development paths. Giving a wonderful alternative for managing and handling data, these models are the manifestation of the “cloud-as-a-service” idea in action. Essentially, the idea is great and you will have three scenarios to choose from. This choice may be made more easily upon finding out under what conditions these models work and in what forms they normally come. Everyone must go through this preparatory, or so-called discovery, stage. It will help you decide on the perfect way of meeting either user needs or business requirements, which will enable utilizing actual resources to the fullest extent.
How does cloud computing work for businesses?
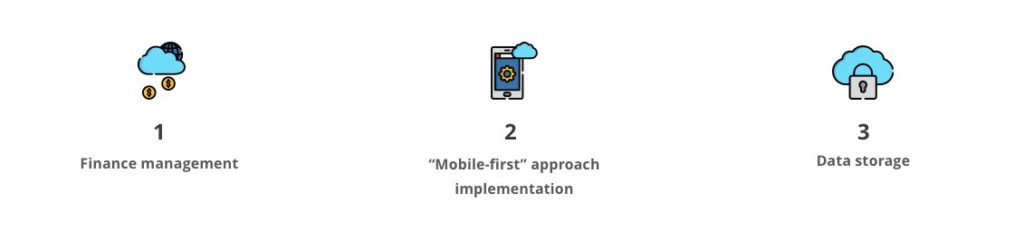
Quite a number of business models are underpinned by the cloud. Accordingly, shopping online and watching videos on YouTube, which most of us are used to doing regularly, are the activities performed through the use of the cloud. It is so because motivation in adopting cloud computing is in the fact that quantities of collected data can thus be entrusted to multiple virtual servers managed by hosting companies. By doing so, you arrange remote storing and on-demand retrieving of data in such a way that the cloud starts working for your enterprise success. Employment of the corresponding service models is, in turn, setting up the prerequisites for taking the following steps:
1. Finance management.
Businesses are facing now the increase in the volume of transactions and their growing complexity. A highly robust financial management system is needed to cope with that. It is a cloud-based solution that will help manage the flow of money and optimize profitability covering as many business processes as never before.
2. “Mobile-first” approach implementation.
Delivering applications to mobile devices by means of cloud computing is another key aspect. Cloud-supported apps do not exploit device resources much so the data is being received from and delivered to various devices running different operating systems.
3. Data storage.
Primarily, the cloud is a place to store information in. Therefore, it is a good idea to rely less on local user devices in an attempt to keep information secure, instead opting for accessing it online and having the backups and syncing done automatically.
Who uses cloud services?
The numerous advantages make cloud services rapidly grow in popularity, and, as a consequence, their fans are legion already. The audience is highly diverse, too. Governments, businesses, and single users recognize how important the cloud is in their daily lives. Besides, they usually prefer combining cloud delivery models. The environment the majority of IT departments around the globe utilizes is reported to be half non-cloud, a quarter of it is SaaS, 16% is IaaS and less than a tenth is PaaS exclusively.
Another opposition appears from the public vs. private clouds comparison. The former type is used by external single customers specifically. It makes up a multi-tenant computing environment, in which data is compiled from multiple sources to be stored in one server. The latter type is, in turn, associated with all forms of organizations and governmental entities since it offers complete or near-complete isolation.
Benefits of cloud computing technology
Regardless of what specifically cloud-computing services are being under consideration, they all present common benefits to derive:
1. Cost efficiency.
Though it is always contextual and rarely granted, the cloud has the potential to become an environment where costs are saved. Saving is made possible by the transition from a Capital Expenditure (CapEx) to an Operating Expenditure (OpEx) model. Under the latter one, expenses are incurred on-demand but not upfront. Thus, you pay just for what is really being in use.
2. An increase in productivity and speed.
Even when there is no possible way to save costs, the cloud still provides the elasticity to the whole experience. Then, it takes businesses little time to get their apps up and running and this approach reduces administration efforts in general.
3. Scalability.
Fluctuating workloads cause no problem to those sticking to any of the three types of cloud delivery models for they all are services that support dynamic scaling. Delivered on-demand, they require no special notifications to be sent to service providers whenever a scalability issue arises, which allows for a consistently optimal performance level.
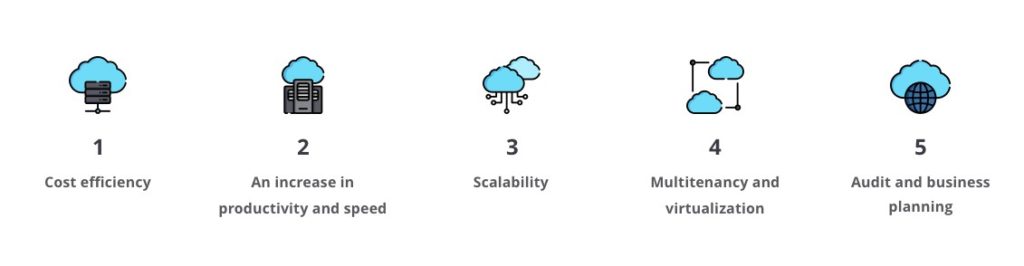
4. Multitenancy and virtualization.
A multitenant model lets clients get infrastructure elements virtualized and managed as a single entity. This entity is deployed in the cloud and customized for multiple tenants. It helps reduce maintenance fees, shorten innovation cycles and improve time to value.
5. Audit and business planning.
Cloud computing technologies automatically monitor and optimize resource usage. Thus, both individuals and organizations can rely on it when they need their data optimized or scaled and responsiveness of businesses improved. With such an intelligent solution, you will save time, reduce errors, and get the planning and reporting process improved.
What is SaaS in the cloud software stack?
Cloud services address different challenges. Still, their intelligence makes any of your investments pay off. Defining what services the cloud computing paradigm comprises, we should highlight the characteristics of each solution — one at a time. We suggest starting with Software as a Service to see how it works.
SaaS key characteristics:
- Fully run and managed by third-party vendors, i.e. hosted on remote servers.
- Provides apps to be installed on client computers and accessed on the Internet.
- SaaS vendor is fully responsible for running software updates.
- Clients pay for software only.
- There is often a chance to test-drive software before paying for a subscription.
- Used in CRM, web-based email, Financial and Customer Service Management.
How does PaaS work in cloud computing?
It is another cloud-based environment in which new web apps and software can be created and deployed faster than on premises.
PaaS key characteristics:
- Provides software engineers with the whole framework for customized app development.
- Nearly all the activities are normally handled by third parties while applications themselves and data are managed by developers.
- App development, testing, and deployment activities are carried out in the PaaS framework.
- The amount of coding is reduced for the creation of highly scalable software.
- No need for programmers to maintain the software later on. Upon uploading it to PaaS, the app is run in that environment.
- The created software is easily migratable.
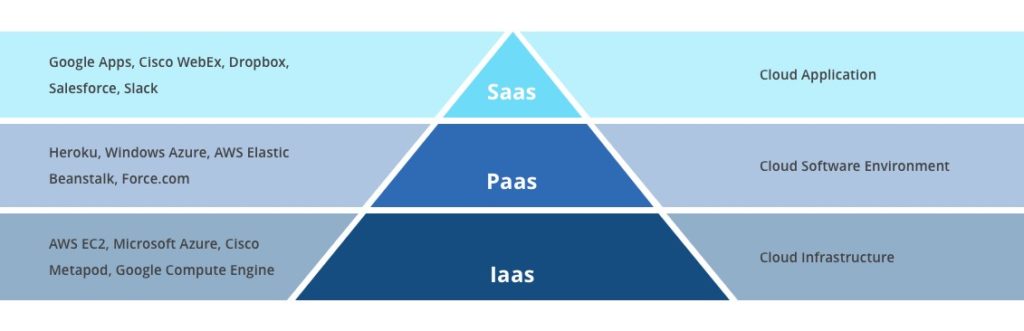
What is Infrastructure as a Service in cloud computing?
As a self-service infrastructure, IaaS enables clients to take control of services like storage, computation or networking but it is only a sliver of the full scope.
IaaS key characteristics:
- Control over the whole infrastructure is in the clients’ hands while service providers are accountable for managing servers, storage, virtualization, and networking.
- IaaS vendors make possible creating, deploying, and managing virtual servers.
- No need for software engineers to spend on hardware, purchases are made on demand.
- It is an extremely flexible and dynamic model to develop scalable software with.
- Examples of Infrastructure as a Service in cloud computing include workload balancing, storage services, monitoring, etc.
Advantages of edge computing over the cloud
A positive contribution the cloud can make to your business is compelling. Nevertheless, as-a-service technologies are not a universal solution. Under certain circumstances, edge computing is a shrewd choice. The edge of the network is thus extending the cloud computing paradigm. Different services are hosted on the computing nodes within the routers. Upon gathering sensory information, such sensor nodes are communicating with one another what they have received creating a network. In view of this, we can safely say that the edge has the following competitive advantages:
1. Sensors in industrial automation.
Implementing sensors is a certain path to the improvement of your business capabilities. This is exactly the case with the industrial IoT. Data coming from the physical world has to be monitored and fully controlled via these applications so that results are generated quickly.
2. Handling huge masses of data.
It naturally follows from the previous point that a huge number of sensors are expected to be used in any given industry. The need in making sense of this information raises the Big Data problem. Shifting to and processing at the edge before sending data to the Internet infrastructure can partially address this problem.
3. Cost efficiency.
With edge computing, workflows can be deployed at reduced costs. In other words, moving to the edge of the network brings resources closer to the end-users. This makes the edge a scalable and agile solution that helps reduce data center costs.
Although computing at the edge holds its potential, the cloud and its services are still more available and mainstream today. One way or another, businesses must pursue their operational efficiency and choose solutions that would serve their needs.
Conclusion
Working in the cloud has many benefits for businesses, governmental entities, and single users. Though types of services provided by cloud computing differ depending on which model you opt for, you are bound to save your time, effort, and other resources anyway.
Using SaaS is the right thing to do when either email or collaborative software is sought. If there is a chance of unpredictable surges, there are multiple software engineers involved or you need a short-term solution, PaaS can meet the requirements. If you are moving from CapE to OpEx or need a solution to assist you when scaling up and down or facing fluctuation, IaaS should be your first consideration. Just know where you stand, be aware of what service models of cloud computing may be in use (with examples,) make your choice and go ahead!

© 2019, Vilmate LLC