Data security is always essential, but today, the issue of cybersecurity is exceptionally pressing. The modern workplace can be a collection of connected devices not limited to a specific physical location. The shift towards digitization and remote access to information in our work methods brings about unique challenges and risks to which we must pay attention.
Additionally, we are witnessing the rapid advancement of artificial intelligence, a concept shaping our online experiences. AI allows cybercriminals to create more complex attacks, automate security breaches, and carry out large-scale cyber assaults, presenting new challenges for existing security systems.
As the information landscape transforms, focusing on measures to protect user data becomes crucial. That's why we will discuss the Zero Trust Model (ZTM) today. We'll talk about the fundamental ideas of Zero Trust, explore how artificial intelligence is used to follow cybersecurity principles, and discover real-life examples of applying ZTM.
Zero Trust Model Fundamentals
John Kindervag, a former Forrester analyst, developed the Zero Trust Model in 2010. Since then, this concept has gained widespread recognition and emerged as the most widely accepted idea in the realm of cybersecurity.
ZTM is based on not trusting anyone, not even users within the network perimeter. It places a strong emphasis on continuously verifying and validating the identities of users. In simple terms, this means that users don't get automatic trust based on where or how they access the network; instead, they must consistently prove their identity. This approach contributes to the creation of a more secure access control model.
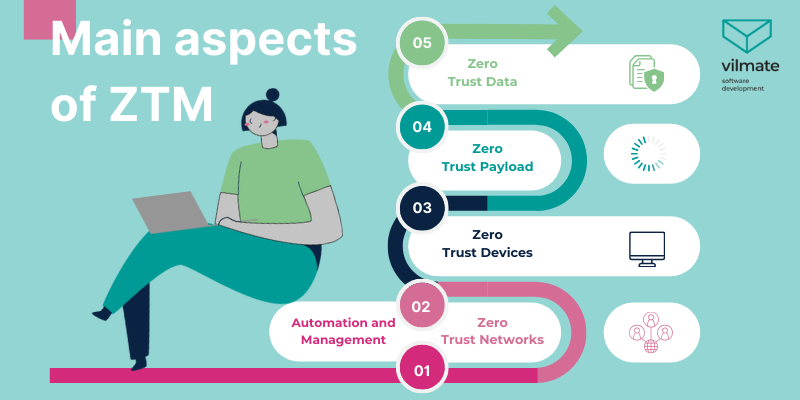
Let's delve into the main aspects of ZTM.
1. Zero Trust Data.
Your data is the target of potential theft by malicious actors. That's why it makes perfect sense that the Zero Trust Model's primary foundation is safeguarding data. This aspect underscores the importance of analyzing, securing, categorizing, monitoring, and upholding corporate data security.
2. Zero Trust Networks.
For attackers to steal information, they must move around within a network. Therefore, your task is to make this process as challenging as possible. The Zero Trust Model requires you to segment, isolate, and control networks using modern technologies like next-generation firewalls specially designed for these purposes.
3. Zero Trust Devices.
With the rise of the Internet of Things, the number of devices in your networks has significantly increased in recent years. These devices can also be potential targets for attacks, so it's essential to separate and monitor them, just like any other computer on the network.
4. Zero Trust Payload.
The term "payload" is used by those overseeing infrastructure services to refer to the entire set of applications and backend software that clients use to interact with the business. Unpatched client applications are a common way for attacks to happen, so viewing the entire technology stack as a potential threat is crucial, and protecting it using tools that align with the "zero trust" concept is vital.
5. Automation and Management.
Automation helps keep all your systems running smoothly with a Zero Trust model and ensures policies are enforced. Handling the volume of events required for the Zero Trust principle is a challenge for people, so automation plays a crucial role in this context.
The philosophy of Zero Trust is more suitable for today's IT environments than traditional security approaches. The diverse range of users and devices accessing internal data, alongside data stored inside and outside the network (in the cloud), makes it safer to assume that no user or device can be fully trusted. It is better than assuming that preventive security measures have covered all potential vulnerabilities.
That's why 61% of organizations claim to have a specific Zero Trust initiative in place today and an additional 35% plan to implement this method shortly.
Thanks to the "never trust, always verify" approach, you can prevent data leaks and other cyber threats. Overall, the Zero Trust Model offers a comprehensive and layered security approach, helping detect and mitigate threats in modern network environments.
By the way, the experts at Vilmate are well-versed in data protection methods and can assist you in choosing and implementing the best approach. Feel free to contact us for advice and further collaboration if you need help.
Now, let's break down different Zero Trust terms and quickly go over the main ones.
Zero Trust Model vs. Zero Trust Maturity Model vs. Zero Trust Architecture
When exploring information about Zero Trust, you may encounter various definitions that can be tricky to understand immediately. So, Zero Trust Model (ZTM), Zero Trust Maturity Model (ZTMM), and Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) are essential concepts in the realm of cybersecurity. Now, what distinguishes them?
We've already talked about the Zero Trust Model, which is a fundamental security principle assuming that no device or user on the network is automatically considered trustworthy.
Zero Trust Architecture is often used instead of ZTM, but it means something a bit different. While the Zero Trust Model is a concept, a philosophy, and a set of principles, ZTA is a specific way of putting this principle into practice through various technologies and architectural solutions. It involves detailed network design, access management systems, monitoring, and other technologies to achieve Zero Trust.
The term Zero Trust Maturity Model is more complex. In 2021, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency in the United States developed the Zero Trust Maturity Model (ZTMM). ZTMM serves as a roadmap for organizations to follow when implementing the Zero Trust principle and helps assess how successfully companies adhere to these principles.
In the National Institute of Standards and Technology guide on Zero Trust Architecture, seven levels of the Zero Trust maturity model are outlined:
- All data computing services and sources are considered resources. Everything connected to the network, including personal devices owned by employees, must be protected.
- Communication remains secure regardless of the network location. Internal traffic should not automatically be considered more reliable than external traffic.
- Access to enterprise resources is provided on a session basis. Each request must be verified and have only the privilege required to complete the approved action.
- Access to resources is controlled by dynamic policies, which consider observed client identification, application/service, requesting assets, and potentially other behavioral and environmental attributes. Setting permission-granting policies should involve multiple relevant factors, especially in the case of automated tasks.
- The enterprise controls and measures the integrity and security of all owned and associated assets. Instead of being allowed to exist in a state of undefined trust, assets must undergo constant assessment for vulnerabilities and signs of compromise.
- All authentication and authorization of resources are dynamic and strictly adhered to before access is granted. There should be a policy and technological solution for re-evaluating access privileges at appropriate intervals.
- The enterprise collects information about the network infrastructure, current state of assets, and communications and uses it to enhance security. Policies should be based on information from current data analytics.
Generally, all three concepts share a common goal: dealing with cyber threats. Now, revisiting the Zero Trust model, let's discuss it in a more up-to-date manner. While the concept itself isn't new, the latest technologies can bring remarkable possibilities to enhance its effectiveness.
AI Revolutionizing the Zero Trust Model
At the article's outset, we highlighted that artificial intelligence introduces new cybersecurity threats. To counter these, it's essential to outpace cybercriminals by employing AI for data protection. This technology is proficient in planning cyberattacks and equally effective in safeguarding data.
Statistics indicate that, on average, data breaches cost companies $4.45 million. Integrating the Zero Trust Model with artificial intelligence can reduce these losses by about $1.76 million.
Let's delve into how AI can modernize the Zero Trust approach.
- Behavioral analytics. It involves efficiently studying user actions by continuously comparing their behavior with established norms. This monitoring happens in real time, enabling the instant identification of anomalies and potential threats. Artificial intelligence is in a constant state of learning and adapting to new patterns. Consequently, it guards against unauthorized access or compromise of user accounts.
- Swift and automated response. AI not only recognizes threats but also efficiently takes action against them. This automated response involves quickly isolating compromised devices, revoking access privileges, or initiating response protocols. By utilizing AI, organizations can promptly neutralize threats, thereby upholding the principles of Zero Trust.
- Adaptive access control. Artificial intelligence dynamically adjusts privileges based on real-time risk assessments. Artificial intelligence considers user location, behavior patterns, and device status. By analyzing user behavior, AI can grant or revoke access to resources, preventing potential cyberattacks.
Incorporating AI into cybersecurity may sound appealing, but how does it work in practice?
Utilizing AI for Zero Trust in Corporate Settings: Real-world Instances
Incorporating artificial intelligence into corporate operations remains a costly endeavor. Despite this, numerous companies are already embracing AI implementation today. Let's delve into notable examples of applying this technology to bolster cybersecurity within the framework of the Zero Trust concept.
1. Identifying potential threats.
ED&F Man, a company involved in commodity trading, faced cybersecurity issues a few years ago. In response, the management turned to advanced solutions. They introduced the Cognito platform, which uses Vectra's AI. This platform is designed to detect and prevent cyber threats by collecting network metadata and using machine learning to identify potential attacks in real time.
The trading company successfully stopped a cryptocurrency mining scheme in Asia thanks to Cognito. It also detected and blocked several "man-in-the-middle" attacks. The artificial intelligence system also identified malware that disrupted the company's operations for several years.
2. Handling sophisticated cyber attacks.
The Energy Saving Trust, an organization committed to reducing carbon emissions in the UK, has incorporated artificial intelligence to enhance cybersecurity within the Zero Trust framework. The company's leadership chose the Darktrace corporate immune system, which utilizes machine learning technology. This platform models the behavior of each device, network, and user to analyze patterns. Darktrace automatically identifies abnormal behavior and notifies the company in real time.
Thanks to this approach, the Energy Saving Trust has identified numerous unusual activities and prevented the risk associated with financial damage.
3. Responsive threat management.
Global Bank faces frequent and sophisticated cyber threats. The organization has turned to artificial intelligence to enhance threat detection and quick response. The Paladin platform serves as an AI-driven detection and response service, improving the bank's ability to prevent data leaks, identify advanced targeted attacks, defend against ransomware, and respond to zero-day attacks.
While artificial intelligence is an excellent solution for implementing Zero Trust, its high cost may limit its use for smaller companies. Therefore, let's explore the initial steps in introducing Zero Trust into a corporate environment.
Guidelines for Integrating Zero Trust into Your Business
Bringing a Zero Trust strategy into play involves a systematic approach and adjustments in the security culture and technological setup. Here are some straightforward steps to assist you in implementing Zero Trust:
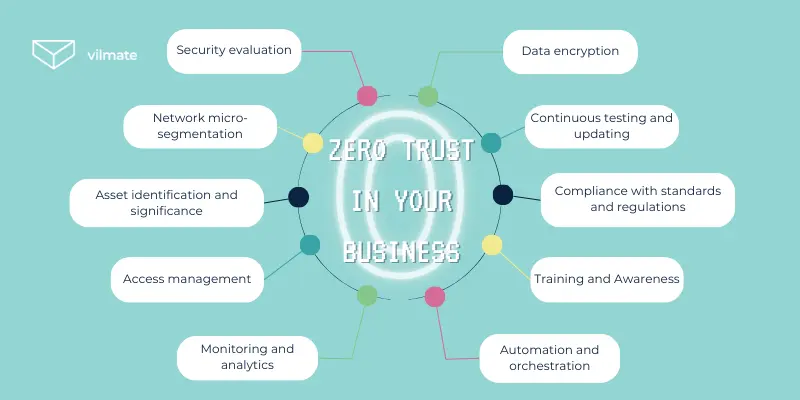
- Security evaluation: Examine and analyze security policies and protective measures, including user authentication and access rights.
- Asset identification and significance: Identify all parts of your network, such as data, applications, and devices, and assess their importance to business operations.
- Network micro-segmentation: Divide your network into isolated sections to limit movement and reduce the risk of attack spread.
- Access management: Implement strict access policies, define who has access to which resources, and enhance security with two-factor authentication.
- Monitoring and analytics: Use monitoring systems to continuously track user and device activity. Apply analytical tools to detect unusual activity and respond promptly to threats.
- Data encryption: Safeguard data through encryption, especially during network transmission. Consider different encryption options for data at rest and in motion.
- Training and Awareness: Conduct regular training for employees and administrators to improve their understanding of security principles and foster a security-conscious culture.
- Automation and orchestration: Introduce automated systems for instant incident response. Use orchestration to automate access management processes and incident response.
- Continuous testing and updating: Regularly conduct security tests, including penetration tests and intrusion checks, and update strategies and technologies to align with evolving threats and the technology landscape.
- Compliance with standards and regulations: Ensure your security approach complies with industry standards and requirements: update strategies in response to legislative changes and evolving security demands.
In general, adopting the Zero Trust approach will demand substantial effort, involving regular updates to systems and ongoing staff training. However, applying these measures is essential to ensuring the comprehensive security of your business data.
Closing thoughts
To successfully introduce Zero Trust into your corporate setup, seeking professional guidance is beneficial. The Vilmate team offers comprehensive advice and solutions tailored to your business's unique needs. We excel at setting up security systems and crafting effective strategies to monitor and respond to potential threats.
We aim to establish a secure environment for your data, reduce risks, and ensure your company operates seamlessly. We commit careful attention at every stage of Zero Trust implementation, starting with auditing your current security and providing support after implementation.





