4 In-Demand Technologies in Telemedicine
articlesartificial intelligenceblockchaininternet of thingstechnologyTelemedicine paves the way for technologically advanced specialty care and high-tech medicine. From real-time consultations and diagnoses aided by ML to wearable IoT devices securely monitoring and transmitting patient data remotely – a world of new and developing cutting-edge technologies are set to significantly impact healthcare delivery in 2020 and beyond. However, finding the right tools remains the continuing challenge for hospitals and doctors in private practice who are eager to find their way around telemedicine.
In this article, we’re going to shed light on what in-demand technologies are best to apply during the telemedicine software development so that the effort and resources taken to create a telehealth solution would justify.
The most promising telemedicine use cases
Before we move on to discussing the best technologies that can enhance your telemedicine solution, let’s first look into how digital information and communication technologies are used in telemedicine. With the help of computers, mobile, and IoT devices, patients can manage their healthcare by accessing these services remotely. At the same time, doctors can significantly improve and support the health service provision and delivery. The following are the most popular ways, in which telemedicine, also called eHealth or mHealth, can be manifested nowadays:

-
Patient portals - an online patient portal is a handy tool used by patients to stay connected with their healthcare providers. It allows patients to see their test results, book appointments, request a prescription renewal or refill, and directly contact their doctor or nurse. The portal can become a more secure place for a customer to share their private medical information. Patient portals are an example of asynchronous telehealth modality in action. Although they effectively facilitate communication, the exchange of data does not happen in real-time: information collected at one point is responded to later on when it is convenient for the recipient.
-
Personal health apps - by only using a mobile phone to access a telehealth app, people can better organize their medical information. With a personal health app, one can upload food logs and keep a record of one’s daily food intake, set pill reminders, and track medication intake. Having another IoT device paired with an app, users should expect to get their opportunities expanded. Thus, for example, these devices help record blood sugar levels, heart rate, and many other medical parameters to send them for review by a nurse who responds electronically afterward. From this it follows that personal health applications also belong in the group of asynchronous telemedicine programs. They are not live and are used primarily to store and transfer images, videos, and other clinical information that a healthcare provider views and responds to at a later.
-
Virtual appointments - this type of consultation is intended to improve care coordination and communication among members of a healthcare team and a patient via an online videoconference. Virtual appointments follow the synchronous modality of care. They take place in real time between the patient and healthcare provider. Appointments are typically scheduled in advance and require the smartphone, tablet, or computer with a camera and a microphone. In rare cases, the consulting medical provider who conducts an evaluation may be located in a place other than the patient, and healthcare personnel – like nurses or nursing assistants who are with the patient physically – uses peripheral medical equipment for more precise health assessment.
-
Remote health monitoring - technologies can empower healthcare providers to monitor patients’ health remotely. This enables the direct communication of medical measurements from a distance to the healthcare provider both in real time and asynchronously. Remote health monitoring is supported by web-based or mobile apps and by devices measuring and transmitting health-related information. Presumably, when individuals monitor their own health, or it is monitored automatically through medical IoT devices, the number of in-person visits to physicians and inpatient stays can drop dramatically. Besides, the customers themselves believe in the power of remote health monitoring. According to the study by Sony’s mSafety Wearable Platform Division, 90 percent of the respondents think a specialized remote health monitoring device can help them better manage chronic conditions. So, the potential of this sphere of telemedicine is immense and must be kept an eye on.
-
Doctor-to-doctor consultations - another way telemedicine can improve the quality of care delivered is cross-border remote second opinions that providers exchange during so-called doctor-to-doctor (i.e., peer-to-peer) consultations. During these second-opinion telehealth consultations, qualified healthcare providers can take better care of the patient’s well-being even if they work for different hospitals or work in private practice geographically far from each other. Besides, this is sometimes the only way for a patient to lawfully get the second opinion on their condition from a skilled professional. In some countries, the direct doctor-to-patient e-consultations and treatment from abroad are forbidden, so a doctor with a local license can become a lawful legal mediator to facilitate communication between the parties.
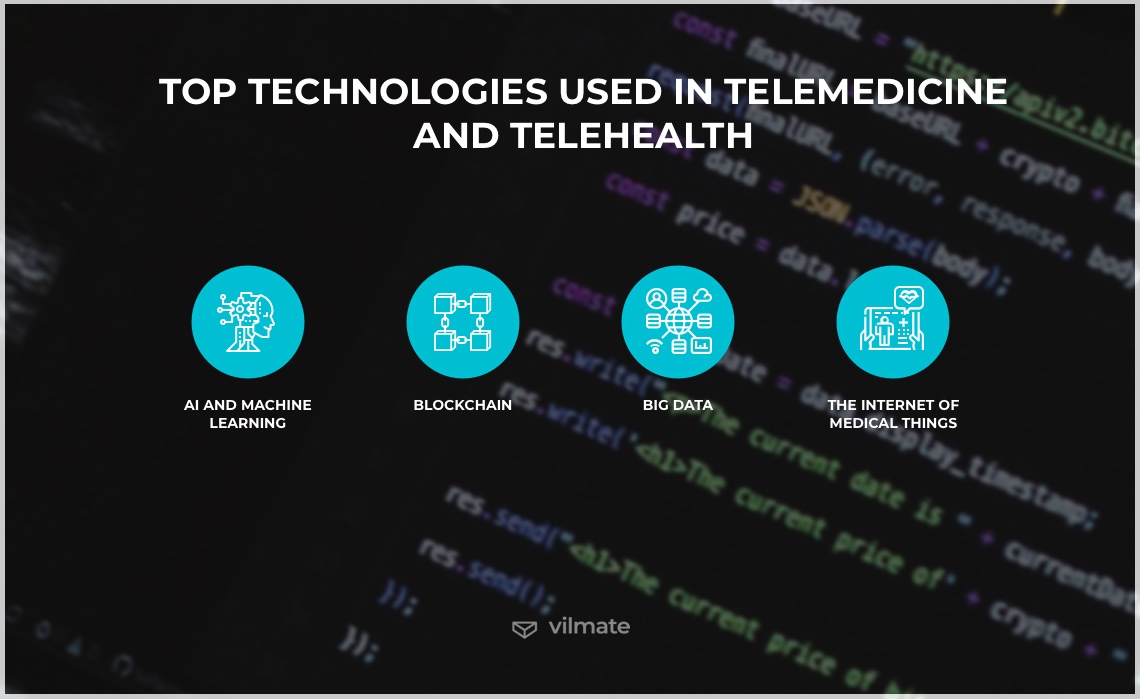
Top technologies used in telemedicine and telehealth
Now that it is clearer when technology can and should become a substantial enhancement of the healthcare delivery process, let’s find out what the most in-demand technologies in telemedicine one has to know about. It must be highlighted, however, that these technological advancements remain relatively costly to implement. Yet, these increased costs can make a huge difference in how successful a given telehealth business is. They hold the potential to drive smart hospitals’ adoption, help clinics and single practitioners alike to save money, and provide the best service possible. The best results should be expected when combining them in one approach, but let’s discuss one technology at a time to better see what positive impact they bring. These technologies are:
- AI and Machine Learning
- Blockchain
- Big Data
- The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
1. AI and Machine Learning
Although Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are not quite the same thing, it will make more sense to discuss them as one in the context of telemedicine.
AI is revolutionizing the healthcare sector so that both pharmaceutical and healthcare companies keep realizing the advantages of AI. Generally speaking, it can significantly increase efficiency and accuracy across the board. AI algorithms can help examine large amounts of medical data to improve the accuracy and speed of diagnosis. In part, it is due to AI that telemedicine has grown to be more than simply using Skype for a doctor and a patient to look each other in the eyes. An effective telemedicine solution means healthcare professionals can receive enough medical data to accurately assess the patient’s health. And AI is here to help optimize the doctor’s time and support the patient before the doctor steps in by giving direction to the user while collecting the data. The technology guides the patient in exactly how to conduct the exam and collect valid data and provides instant feedback on whether a photo or a video clip taken by the user has high enough diagnostic quality. It also enables an auto-capture feature, helps deliver therapy on the patient’s side, and empowers triage software that physicians can use to the order in which patients need care.
The role of Machine Learning here is to derive insights from incoming blocks of data and allow healthcare providers to arrive at the correct decisions faster. As a result, the technology will augment human decision-making, take over more mundane tasks, and help bring medical expenses down.
2. Blockchain
Blockchain technologies can be used in telemedicine to ensure profoundly secure data transferring and storage. Security is of paramount importance in the healthcare industry, so providers must take every precaution to avoid breaches or leaks of sensitive health data and other patients’ information.
Blockchain is known for its immutable ledger and cryptographic design. This all places the technology in a powerful position to protect telemedicine services. Having all records and transactions stored on blockchain, telehealth solution providers can address many of the alarming challenges related to online healthcare. First and foremost, secure, fragmented blockchain-enabled systems are a better place to contain large amounts of data that doctors need to access a complete patient history. All medical records are signed and securely encrypted, which gives patients the confidence that their records won’t be modified.
However, before blockchain-driven telemedicine becomes a widely accepted practice among patients and healthcare professionals, a number of technological vulnerabilities and barriers must be addressed first. These include the high cost, the lack of industry expertise, and the insufficiency of standardization.
For instance, HIPAA includes guidelines concerning data transfer security, which means data encryption with blockchain must also remain compliant. But at the same time, these rules apply only to covered entities, not to patients. This lack of interoperability may result in the limited ability of platforms to connect to one another. Nevertheless, as the benefits of blockchain for telehealth are being more widely acknowledged, all these challenges will be surpassed, and the robust cybersecurity will become a default property of every telemedicine solution.
3. Big Data
Big data technologies help healthcare providers meet the goal of turning high volumes of information into actionable knowledge for the customization of healthcare within the framework of precision medicine. Once all the available data associated with a patient’s health history is collected, a doctor can delve into the context, see the big comprehensive picture, and go on with more precise decision-making and better-coordinated treatment.
The impact of big data analytical techniques, platforms, and tools on healthcare organizations practicing telemedicine is immense. They allow the transition from the disease-centric model to the patient-centric one. From the perspective of big data, a patient-centric ecosystem involves collaboration between stakeholders like insurers, medical practitioners, service providers, and pharmacists who openly share data insights for the patient’s good. Besides, this personalized healthcare model can benefit from collaborative filtering – capturing patients’ similarities (e.g., demographic data, family history, occupation, symptom, lab result, etc.) and providing proactive healthcare solutions in the context of big data.
As a result, supported by ICT based mHealth, eHealth, Smart Health, and telehealth devices, big data technology exhibits ample potential for streamlining such healthcare functions as disease surveillance, clinical decision support, and population health management. Meanwhile, the impact of big data in healthcare is getting even more substantial due to the emerging new sources of information like social media platforms, telematics, and wearable devices. This brings up an issue of the challenges that the introduction of big data analytics in telemedicine entails. Most of the challenges that the use of Big Data in telehealth poses arise from the personal nature of the exchanged information and have ethical and legal nature. The popular demand for transparency can sometimes be at odds with the risks to compromise privacy and personal autonomy, as well as concerns about the commercialization of data and using it against the interests of the people providing it. However, the longer big data technology is present on the telemedicine market, the easier it will be to overcome the obstacles.
4. The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
Now we have arrived at perhaps the most critical technology that one can possibly incorporate into their telemedicine solution the Internet of Medical Things, or IoMT. With the forecasted worth exceeding US$ 136.8 billion by 2021 and reported 3.7 million IoMT devices currently in use, the IoMT sector is fueled by an increase in the number of convenient patient-centric connected medical devices that collect, analyze, and transmit data to healthcare IT systems.
IoMT-related tech products and services (telemedicine mobile apps) enable ongoing health status monitoring and on-time discussion of any concerning issues with medical providers. IoMT is powered by a collection of medical devices that are equipped with wireless communication capabilities. This means communication among machines and between devices and cloud platforms where data is stored looks effortless to the human eye. As a result, cardiac monitoring, blood pressure or glucose levels measurement, weight control, and many more healthcare-related tasks can become no problem for everyone. IoMT also offers chronic disease monitoring and general physical well-being improvement, for example, by assisting patients with degenerative diseases in their exercises with the help of mobility sensors IoMT wearables are outfitted with. In other words, the Internet of Medical Things devices can empower patients to analyze and report data without visiting a doctor.
All in all, the technology is gaining ground. The more large-scale interoperability and interpretation capabilities of IoMT are yet to be discovered. Still, even as of today, it is clear that there is potential for significant changes in the telemedicine industry.
Conclusion
The successful application and evaluation of digital tools can improve access to better-coordinated care for everyone. This is the ultimate goal of the telemedicine technologies application. And although their potential of AI, Blockchain, Big Data, and IoMT for telehealth has not been realized yet, the room for action keeps expanding.
As of today, the challenges that the introduction of the technologies under discussion poses are being studied and thoroughly analyzed, just like the benefits and capabilities are. So, while the exploration is ongoing, don’t miss your chance to contribute to the future of digital health. Share your idea with us, and we’ll help you create a telemedicine solution empowered by one of the most in-demand technologies in the telehealth industry.

© 2020, Vilmate LLC