During the 1990s, the Internet experienced a rapid surge in popularity, and computers became a common sight in ordinary households. This fact marked the advent of the Digital Age, a profound transformation that permanently altered our way of life. More than half of the global population is now connected to the Internet, with computers, smartphones, and IoT devices granting us a thriving online existence.
While people have always valued their privacy in the physical world, nowadays, not everyone treats online data security with the seriousness it deserves. Nonetheless, safeguarding digital data is paramount, and users and companies offering online services should prioritize it. That's why this article will delve into the realm of online confidentiality.
What is online privacy?
Have you ever pondered the true significance of “online confidentiality” concerning you? What sort of data would you be comfortable entrusting to strangers? Undoubtedly, you’d want to safeguard sensitive information such as bank card passwords and your home address from malicious individuals’ hands.
Perhaps you’d like to keep information about your online purchases and phone number private. However, all this data may already be circulating in the digital realm. The crucial question remains: how well is it shielded from prying outsiders?
The online world’s boundary between “personal” and “public” is blurred. Nevertheless, the fundamental principle of online confidentiality is ensuring that your data only fall into the hands of those you willingly trust.
For instance, if you post a photo on a social network, you know anyone with internet access could see it. At the same time, you wouldn’t want everyone to know your bank card details but trust that information in your bank’s application because you know it will be well protected.
The protection of personal data is indeed a complex task. As we navigate the online world, we unknowingly leave behind digital footprints that can be collected, analyzed, and exploited without our consent. These digital footprints become valuable assets for various entities, ranging from advertising agencies and marketing companies to governmental bodies and cyber criminals. Our personal information, including location, purchases, search queries, social media messages, and even biometric data, has become highly sought-after in the digital marketplace.
Numerous technologies, such as cookies, trackers, tracking pixels, and machine learning algorithms, facilitate the collection and analysis of our data, enabling personalized services, targeted advertisements, and improved user experiences. However, this process also risks our online privacy, as our data can be compromised, and we may unknowingly become victims of unethical data usage.
Some companies and organizations prioritize data protection for their users and clients by implementing strict privacy policies and adhering to relevant laws and standards. Despite these efforts, it isn’t always possible to fully control how third-party services process and share our data or, more importantly, how they utilize it in the future.
The issue of safeguarding online privacy also holds significant importance at the governmental level. Some countries have strict laws and regulatory measures to govern the collection and processing of citizens’ data. In contrast, the regulations may be less stringent or non-existent in other regions.
For instance, the European Union has implemented the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), which took effect on May 25, 2018, and serves to regulate the protection of data and the privacy of its citizens. GDPR empowers individuals with greater control over their data and imposes obligations on organizations that gather, process, or store such data.
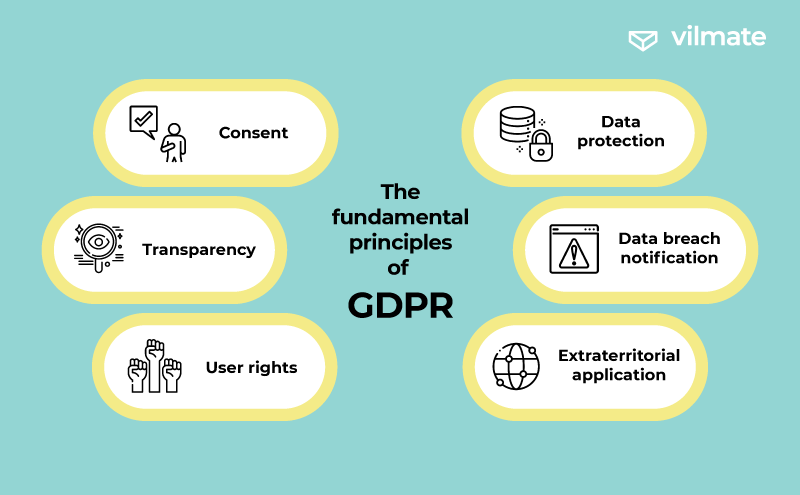
The fundamental principles of GDPR include:
- Consent: Organizations must obtain explicit, informed, and freely given consent from users before collecting and processing their data. Users have the right to withdraw their consent at any time.
- Transparency: Organizations are required to provide users with clear and accessible information about the purposes and methods of using their personal data.
- User rights: GDPR grants individuals several rights, such as access to their data, correcting inaccuracies, being forgotten (i.e., having their data erased), restricting processing, and data portability.
- Data protection: Organizations must implement measures to protect users’ data against unauthorized access, loss, or destruction.
- Data breach notification: Organizations must promptly notify the relevant authorities of a security breach that may threaten individuals’ rights and freedoms.
- Extraterritorial application: GDPR applies to all organizations that process data of EU citizens, even if those organizations are based outside the EU.
Non-compliance with GDPR can lead to significant fines for organizations, up to 4% of their global annual turnover or €20 million. GDPR aims to safeguard personal data and increase user confidence in handling their information, promoting a more responsible and transparent approach to data protection in the digital world.
Companies need to prioritize user security not only because of GDPR but also due to reputational risks. Significant data breaches of personal user information can lead to substantial scandals and a loss of user trust. However, many big companies tend to be overly cautious, and instead of guaranteeing protection for all data, they require users to agree to its usage. Hence, let’s delve into the concept of a privacy policy.
Privacy policy: what are companies hiding?
A Privacy Policy outlines how a company intends to use your data. Typically, this document doesn’t specify how the company plans to protect this data.
Have you ever checked the “I agree to the Privacy Policy” box without clicking the link to read the document? According to research, 87% of people do precisely that. Some claim that reading the document takes too much time, while others admit they don’t understand what’s written. And it's not surprising, considering that many security policies are quite long and written in intricate legal language. The most extended and convoluted privacy policies are on TikTok, WhatsApp, and LinkedIn.
Professor Jonathan Obar from York University in Toronto and Anne Oeldorf-Hirsch from the University of Connecticut wrote “The Biggest Lie on the Internet,” dedicated to their social experiment. In the experiment, they created a social network called NameDrop and invited students from different colleges to register. In the Privacy Policy of this social network, there was section 2.3.1, stating that users must give NameDrop their firstborn child.
All 543 students who clicked the “join” button accepted this condition. None of them read the terms of service to see the catch. The experiment highlighted an important issue: users don’t read the privacy policy. One of the main reasons is the pages’ design and the invitation’s wording to read. However, only some companies attempt to address this problem since they benefit from users agreeing mindlessly. So, what are companies hiding from us?
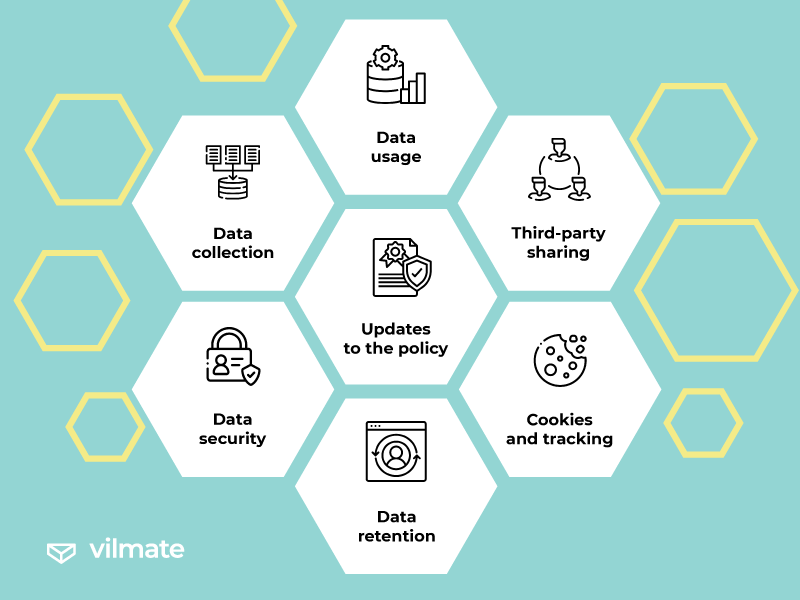
Some common points covered in these agreements that often go unnoticed by users include:
- Data collection: Companies specify what types of data they collect, including personal information like names, email addresses, phone numbers, etc. They may also collect data on users’ browsing behavior, location, and interactions with their services.
- Data usage: Privacy agreements outline how the company will use the collected data. It may include improving their services, targeted advertising, market research, personalization of content, and more.
- Third-party sharing: Many companies share user data with third-party service providers, advertisers, or business partners. It could involve sharing data for analytics, ad targeting, or other commercial purposes.
- Cookies and tracking: Companies may use cookies and other tracking technologies to monitor users’ activities and gather information about their online behavior.
- Data retention: Privacy agreements often state how long user data will be retained by the company, which can vary depending on the type of data and the purpose of its collection.
- Data security: Companies may briefly mention their security measures to protect user data, but the level of detail provided can vary significantly.
- Updates to the policy: Companies reserve the right to update or change their privacy policies at any time, and it’s the user’s responsibility to keep up to date with any modifications.
Indeed, many users visit numerous websites per day, and almost all of them require accepting their terms. Reading so much tedious, lengthy legal information is something no one can handle. Therefore, several crucial aspects need special attention in the privacy policy:
- Data exchange and selling
- Collection of biometric information (health data, photos)
- Disclosure of information to law enforcement agencies.
We also recommend paying close attention to two specific phrases: “improvement of products and services” and “mergers or acquisitions.”
The first phrase implies that your data may be used for machine learning or artificial intelligence. For example, your photo might be used to train a facial recognition program. Even if you don’t mind providing your data for training, it’s better to be aware of this fact.
The phrase “mergers or acquisitions” means the company will transfer all your data collected over the years to the new owner. And it’s not guaranteed that you’ll be happy with these changes.
Nevertheless, not all companies intend to deceive or hide information from users.
Good examples of privacy policies
Having a privacy policy is mandatory for all, but it doesn’t necessarily mean there’s something to hide. Some companies explain their privacy policies in clear and straightforward language.
Zoom, Arlo, and Apple are among the most renowned companies that have set a great example with their privacy policies. While standard agreement terms may appear straightforward, these companies provide dedicated pages with vibrant designs.
Apple, in particular, builds much of its PR campaign around user data protection and even offers the slogan: 'Privacy is a fundamental human right.' In addition to clearly explaining their data handling practices to users, Apple also takes measures to protect users from being tracked by apps and websites. For instance, the company requires apps and websites to request user consent through notifications before using specific information.
It’s essential to note that a company should not only invest time in crafting a privacy policy but also ensure the security of user data. Understanding the risks that may arise if the company you trusted experiences a data breach is paramount.
The danger of confidential data leaks
We have heard of numerous high-profile scandals involving massive data breaches. Companies face reputational damage each time, pay fines, and may meet legal liabilities.
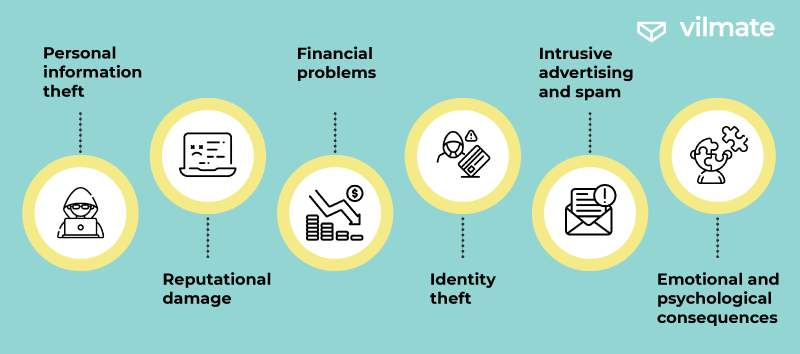
However, users should not solely rely on companies and mindlessly accept privacy policy terms. We have compiled a list of significant and minor risks that users take when entering data online:
- Personal information theft: Hackers or malicious actors may gain access to personal data, such as names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, social media accounts, and more. This data can be used for fraud, identity theft, spam, and other unlawful activities.
- Reputational damage: A leak involving confidential information or compromising content can harm an individual’s reputation personally and professionally.
- Financial problems: Data breaches involving financial data (e.g., bank details or credit card numbers) can lead to financial losses due to unauthorized transactions.
- Identity theft: Criminals can use stolen personal information to commit identity fraud, open new credit accounts, or engage in other crimes on behalf of the victim.
- Intrusive advertising and spam: Data leaks may result in receiving intrusive advertisements and spam through email or phone, which can be irritating and unpleasant.
- Emotional and psychological consequences: Those affected by confidentiality breaches may experience helplessness, anxiety, and stress, especially if the leak involves sensitive information.
Besides hackers and marketers, countries’ governments may also be interested in users’ data. Confidential information can be used for surveillance, control, or decision-making.
In early 2023, there were at least three significant data leak scandals:
- It was revealed that TikTok unlawfully processed data belonging to 1.4 million children under 13.
- Yum! Brands experienced an attack in which malicious actors stole user data, including names and identification numbers.
- Hackers breached the Cody Fund and gained access to the private conversations of 400,000 users.
All these significant events occurred within a few months, causing considerable damage to the brands’ reputation and their customers’ security. Therefore, in the following discussion, we will address what users and companies must do to protect confidential data.
How to protect confidential data?
First, let’s discuss what users can do to prevent their confidential data from falling into the hands of hackers, intrusive marketers, and others.
Here are some advices that will help you safeguard your data:
- Check the privacy policy: Before using new online services, read their privacy policy to understand how they handle your personal information.
- Strong passwords: Use unique and complex passwords for each online account. Passwords should consist of a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Two-factor authentication (2FA): Enable two-factor authentication wherever possible. It adds an extra layer of protection, as you’ll enter a one-time code received on your phone in addition to the password.
- Software updates: Regularly update your operating system, applications, and browsers to leverage the latest vulnerability fixes and security updates.
- Internet caution: Be cautious about what you share on social media and public forums. Never disclose personal information or data that could be used for identification.
- Use secure Wi-Fi networks: Avoid connecting to open or unsecured Wi-Fi networks, especially for critical operations like banking transactions or password input.
- Be vigilant about emails: Exercise caution with phishing emails; don’t open suspicious attachments or click on links from unknown sources.
- Limit permissions: Applications and services may request access to specific data on your device. Refrain from granting access to unnecessary information.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): Use a VPN when connecting to public Wi-Fi networks to provide additional security and privacy.
- Regular activity monitoring: Regularly check your online accounts and banking transactions to detect any unusual activity quickly.
Complying with these recommendations will help enhance the protection of your confidential information and reduce the risk of encountering problems due to data breaches on the Internet.
On the other hand, companies need to be honest and transparent with their users. Collecting information about customers should not result in reputational losses. It’s also crucial to provide users with tools to safeguard their data. For instance, companies can disallow weak passwords on their websites and enable two-factor authentication. Additionally, corporations are obligated to prioritize cybersecurity.
Below are several essential methods for safeguarding user data that they can employ:
- Data encryption: Encrypting confidential data both in transit and at rest to prevent unauthorized access.
- Monitoring and auditing: Regularly monitoring network activity and auditing the system to detect unusual activity or security breaches.
- Malware protection: Installing antivirus software and other malware protection tools to prevent and detect incidents.
- Physical access protection: Ensuring physical protection for servers and equipment containing confidential data.
- Data backup: Regularly creating data backups to prevent information loss in the event of system failure or cyberattacks.
- Incident response: Develop security breach response plans and promptly respond to potential incidents to minimize harm.
By following these measures, companies can reduce the risk of data breaches and safeguard their customers’ confidential information, building trust and maintaining a solid reputation among clients and partners.
Final words
Recognizing the importance of data privacy in the online realm drives us to employ cutting-edge methods and technologies to ensure data security. Our seasoned cybersecurity specialists are committed to tailoring strategies to meet each client’s unique needs. If you need assistance crafting a robust cybersecurity strategy, you can always rely on Vilmate’s team of experts.
Having a vast IT development and cybersecurity expertise, we offer various services to secure our clients’ sensitive data. We adopt a comprehensive approach to data protection, encompassing thorough staff training, implementation of advanced encryption technologies, and establishment of robust policies and procedures to uphold high security.
Moreover, our team actively assists clients in developing software, always mindful of security and data protection principles. Our ultimate goal is to create robust and reliable applications that guarantee our client’s information’s security and confidentiality.