In May 2017, the European Commission published the final version of the Medical Device Regulation (MDR). After being in development for several years, the document is now meant to replace the previous European Union’s Medical Device Directive that had been in force since the 1990s. Once the regulation has been finally agreed upon, the transition end date from the European Medical Device Directives to the new EU MDR was set for May 26, 2020. However, in the light of the 2020 pandemic, the European Commission arrived at the decision to defer it from taking effect until 2021.
One of our clients has undergone the MDR compliance audit, and so have we, Vilmate, as a service supplier. Since we still have the whole year ahead, let’s research into the topic and find out what the introduction of the MDR implies, what consequences it will have for medical device manufacturers and software development vendors, and how they can prepare for the changes.

What does MDR mean for software development?
EU MDR is a large-scale regulation. Unlike directives that everybody is free to decide how to transpose, regulations, as such, have a binding legal force. In the case of MDR, it will be in effect throughout all EU member states. So, it will be mandatory for ALL new medical devices to pass the testing.
Essentially, the Medical Device Regulation will require all medical devices sold in the European Union to undergo testing at the EU level. However, not only will the new rules influence device manufacturers. The use and development of medical device software applications is also going to be regulated. MDSW that is not intended to be used in clinical decision making falls under Class I of MDR, those that do – Class II and III. And for medical software functions to be considered a medical application covered by the regulation, they must meet the definition of a device. In this context, it must be emphasized that not any piece of medical software falls under the definition of a medical device.
Meanwhile, the performance spectrum of these apps may be sufficiently broad to include assistance for people in managing their health and wellness, gaining access to useful health-related information, and promoting healthy living, as well as automation of simple tasks for health care providers.
When serving these functions, sometimes, there is a chance that a medical software app can pose a risk to patients unless the appropriate audit has been undertaken to ensure the opposite. So, the MDR is a document that has been designed to help authorities exercise oversight over such device software functions so that the risk wasn’t there in the first place. And if there are vulnerabilities or faults, MDR has to prevent the misuse. The Medical Device Regulation is all about the importance of patient safety, service transparency, and process traceability.
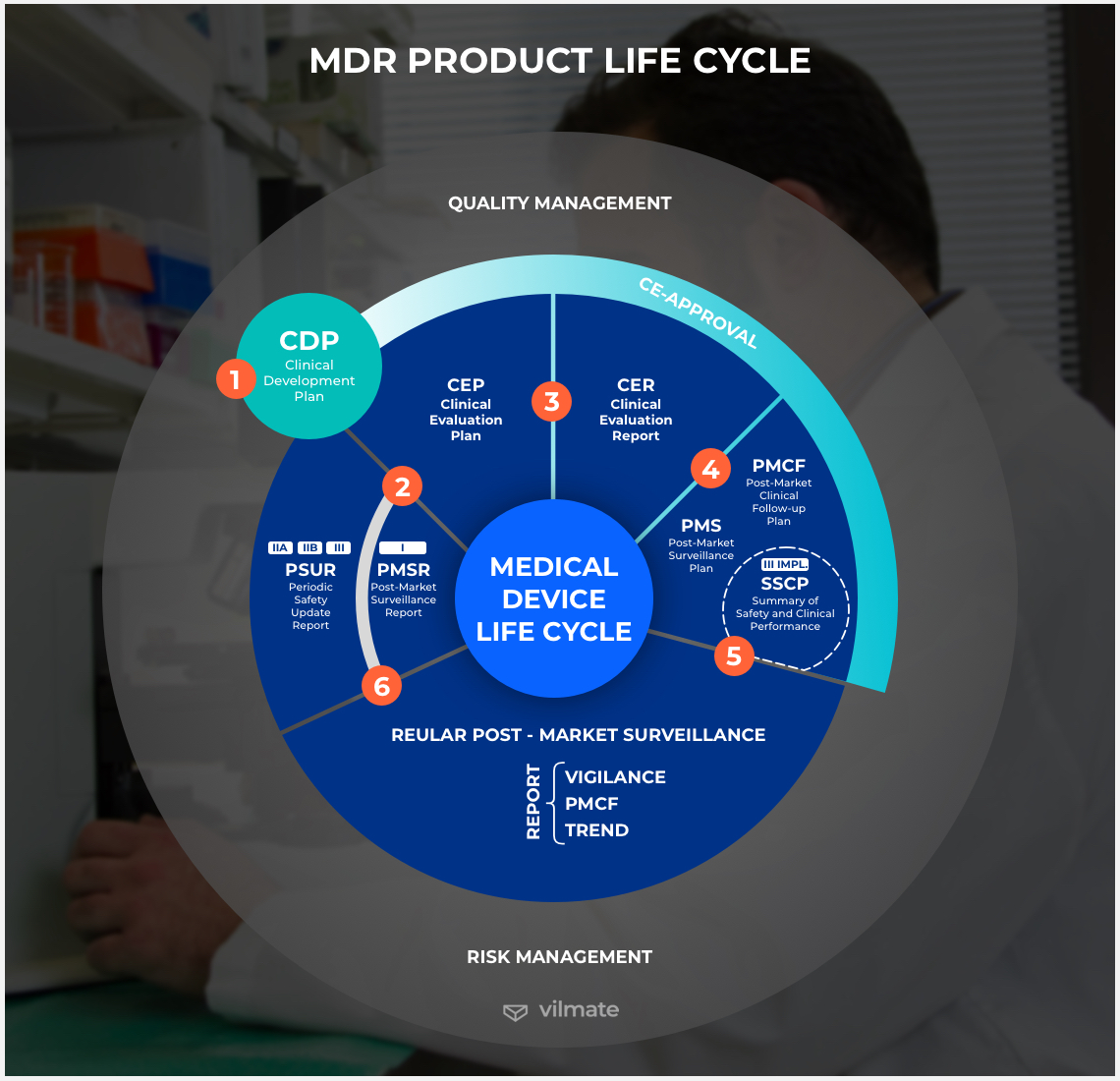
Essential requirements under MDR
The MDR is needed to monitor and oversee the development of medical software systems. And this will give patients an assurance that everything is being done in a fair, safe, and ethical way. Although the regulation’s implementation date was postponed, it will still be one of the few regulations that truly supports fair and just medical technology. Under this regulation, the following requirements will have to be complied with by every medical device manufacturer and software vendor in the European Union:
1. When deciding on the intended use - To begin with, one has to provide proofs that the product can be considered a medical device, define what class it refers to, and make it clear how exactly the app is going to be used – what the customer’s need is and what the end-users are going to be able to achieve.
2. When establishing processes and resources - Another important preparatory step to ensuring MDR compliance is to come up with a clear and concise plan for the potential resource use during product development and implementation. It includes clarification of who will develop a device, how it is going to be distributed, and how customers will be able to receive support. Risk management, clinical evaluation, technical documentation development, quality management, and post-market surveillance plan development also have to be taken care of.
3. When ensuring safety - A medical software provider must at all times be able to offer safety through undertaking all the necessary risk management activities. The post-market surveillance requested under the MDR is anticipated to be stricter. So, more rigorous clinical evidence, unannounced device audits, as well as annual safety and performance reporting, must be expected as part of the MDR.
4. When performing a clinical evaluation - As it was implied in the previous points, MDR emphasizes an entire-cycle approach. So, instead of receiving a pre-market approval and moving on, manufacturers and developers must ensure compliance with the regulation at every step of the process and control the whole lifetime of their medical device. Thus, a clinical evaluation plan has to be designed with a view for a long-term execution.
5. When handling tech documentation - The fact that medical devices and related medical software must obey the new regulation means that there is also going to be a lot of documentation to ensure compliance. Preparation and review of compliant technical file documentation for medical device software products are going to become a crucial part of the process. When handling tech documentation, one has to refer to the information set out in Annexes II and III to the MDR.
6. When arranging product distribution - Among others, the MDR transforms the scope of the responsibilities that medical device manufacturers are obliged to fulfill in connection with product distribution. In particular, after MDR’s taking force, it will be manufacturers who will have to control whether the distributed product is compliant. When in doubt, distributors will be free to enquire of the manufacturer or importer about the product’s compliance with the regulation.
7. When completing registration - Articles 29 and 31 of the Medical Device Regulation provide a detailed explanation of how to register medical device software applications. A manufacturer, its authorized representative, or a product importer must obtain a single registration number via submitting economic operator information. Then, using the SRN, they submit device-related information to the European database on medical devices. In general, a collection of data sets that must be provided in EUDAMED becomes much more significant than it used to be.
8. When assessing product conformity - Under certain conditions, this step may be skipped by the manufacturers of Class I devices. Otherwise, manufacturers whose Class I devices are not sterile, reusable, or have a measuring function may choose to turn to a notified body or competent authority and ask them to perform a conformity assessment. For everybody else, it is obligatory to go through the conformity assessment procedure. They must get a number of EU-level quality certificates from a notified body.
9. When finalizing administrative procedures - After all required certificates are at hand, the EU Declaration of Conformity is finalized, and other technical documentation is in order, a manufacturer can and must register its medical device. If needed, an authorized representative and an importer can do so, too. Importantly, currently approved devices must be recertified in accordance with the new requirements as well. Then, the packaging and instruction must be published in a national language, and if there is a website, these national-language versions must also be posted there.
10. When maintaining the product after its launch - Under the MDR, a manufacturer must maintain its medical device and the corresponding software application all the time as part of post-market surveillance. Throughout the life of the product, the manufacturer has to diligently maintain the state-of-the-art, regularly perform post-market clinical follow-up activities, keep the tech documentation up-to-date and available for the EU authorities, improve quality management, support the post-market surveillance system activities, react immediately to the emerging poignant issues and report them to authorities.
Conclusion
The Medical Device Regulation is not only the innovation that has shattered many medical device manufacturers and software vendors across the European Union. In the first place, it is a considerable improvement to the existing outdated declarations, which is meant to refine the quality of service for customers, as well as ensure their safety and security in the digital age. That, in turn, is going to nurture trust between the manufacturer and the clientele.
The MDR is a significant change, and it is imperative to get ready for this change – go through all the steps to the MDR compliance that we’ve highlighted and prove that you are a professional who respects and values its customers and realizes the responsibility of supplying products that meet the safety and security requirements to the public.

© 2020, Vilmate LLC




