We have locks and alarms to safeguard our boundaries in the physical world. The online realm has its virtual boundaries that keep our digital assets and sensitive data safe. As businesses expand their presence on the internet and increasingly rely on digital technologies, ensuring robust protection against cyber threats becomes imperative. Here, cybersecurity is a guardian that shields the virtual space from cybercriminals, hackers, and other undesirable activities.
The significance of cybersecurity cannot be underestimated, as inadequately secured systems and vulnerabilities in the online world can have far-reaching consequences. Data breaches, intellectual property theft, and disruption of critical infrastructure can cause substantial harm to both individual organizations and society.
However, cybersecurity isn’t merely a precautionary measure but also an opportunity to foster trust in the online realm. Users feel comfortable and confident knowing their personal data and financial information are protected while conducting online transactions.
In this article, we will delve into the realm of cybersecurity and explore its role in the budget planning of companies. We will discuss hackers, who can organize into formidable groups, and the most prominent cybercrimes of the 21st century. Nonetheless, let us begin by addressing the central question: what is meant by cybersecurity?
Basics of cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is a field of knowledge, practices, and technologies to protect computer systems, networks, software, and data from digital attacks. It deals with ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information and preventing unauthorized access, cybercrime, and other types of cyber threats.
Within the realm of cybersecurity, various technical and organizational measures are employed. These include strong passwords, data encryption, multi-factor authentication, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, etc.
The primary goal of cybersecurity is to prevent data breaches, which can lead to significant financial expenses, reputational damage, and even criminal liability.
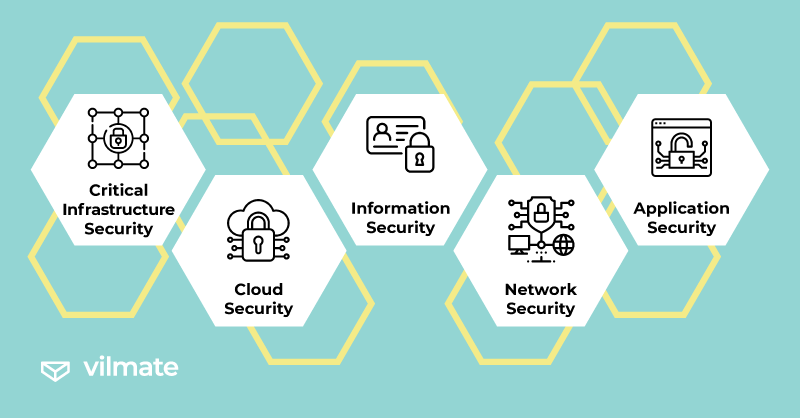
There are several key cybersecurity measures:
- Critical Infrastructure Security protects networks and computer systems crucial for national security, economic stability, and other vital functions. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) regulates essential aspects in this field.
- Cloud Security encompasses measures to protect cloud data during storage, transit, and usage. Cloud security ensures the safeguarding of confidential customer information.
- Information Security focuses on safeguarding user data, preventing unauthorized access, theft, and exposure. In Europe, information security is regulated by the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which must be adhered to by companies offering IT products.
- Network Security encompasses processes that protect wired and wireless (Wi-Fi) connections.
- Application Security involves measures to protect both local and cloud-based applications. Application security is integrated into product design and considers data processing and authentication aspects.
Furthermore, user education plays a crucial role in cybersecurity. Companies and governments prioritize raising awareness among clients about potential cybercrimes. For instance, users are educated on identifying suspicious emails, recognizing phishing websites, and avoiding connections to unknown USB devices.
An essential aspect of cybersecurity is the development of disaster response plans. Even during power outages and unforeseen events, data must be securely preserved.
Now let's discuss the main types of cyber threats.
- Malware
- Phishing
- DDoS Attacks
- Insider Threats
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APT)
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
It encompasses various types of malicious software, including trojans, viruses, worms, and spyware. Such applications infiltrate users' devices to gain access to information or cause harm. Antivirus programs are used to combat malware, but hackers continually find ways to bypass protection. Ransomware, a prevalent type of malware, blocks system data. Cybercriminals demand a ransom, threatening to delete or make the data public. Government agencies, websites, and quickly hackable applications have become frequent targets of ransomware attacks.
It’s a form of social engineering that involves deceiving users. Cybercriminals create phishing websites or send emails posing as legitimate, often well-known, companies. Phishing aims to extract confidential data, often including credit card information or login credentials. Phishing has become particularly widespread during the pandemic.
These attacks attempt to overload servers, websites, or networks with traffic to render them inoperable. DDoS attacks flood corporate networks using the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). This cyber threat is often used for competitive elimination or extortion.
This type of cyber attack originates from former employees of corporations, contractors, or partners – -essentially, anyone who has ever had access to company data. Insider threats are dangerous because they remain invisible to standard security systems, which are often more focused on external threats.
In this case, cybercriminals infiltrate a system and remain there without taking immediate action. The perpetrators don’t immediately harm the system or network; instead, they spy on business activities or steal information without triggering countermeasures.
This attack involves eavesdropping, where an attacker intercepts messages between two parties to steal data. It's crucial to exercise caution when connecting to public Wi-Fi networks due to such attacks.
As you can see, there are various cyber threats online. But who engages in cybercrimes? The average person often envisions hackers, as portrayed in numerous movies. Let's talk a bit about them.
A hacker doesn't necessarily have malicious intentions to hack into your system and steal all your data. That's why these individuals are generally categorized into three groups.
White hats
White hats, also known as "ethical" hackers, are specialists who actively seek out security vulnerabilities to help companies improve their systems. They play a crucial role in reducing website issues for organizations. It's important to note that white hats operate with full permission from system owners, and their actions are entirely legal. They employ standard hacking methods while adhering to ethical guidelines. Some of the most prominent members of the white hat community include Tim Berners-Lee, the creator of the World Wide Web, Richard M. Stallman, the founder of the GNU project, and Charlie Miller, the individual who discovered vulnerabilities in Apple's systems.
Black hats
Black hat hackers are criminals who engage in illegal hacking activities. They create malicious software, infiltrate systems, and generally cause harm to the cyber realm. Their motivations include financial gain, revenge, or simply causing chaos.
The most famous black hat hacker is Kevin Mitnick, who was once the most wanted cybercriminal in the world. He has targeted over 40 organizations, including Motorola and IBM. Kevin served a lengthy prison sentence and later became a cybersecurity consultant.
Gray hats
Gray hat hackers walk the line between good and evil. They search for vulnerabilities in security systems without obtaining permission from the system owners. However, they refrain from using the acquired information for malicious purposes and instead, inform the organization about the issues. Gray hat hackers may request a small fee for mitigating the cyber threat.
While gray hat hackers don’t commit major crimes, their actions are still considered unethical. Often, these individuals act to gain publicity and recognition within the hacker community — for example, Khalil Shreateh, who hacked Mark Zuckerberg's Facebook page. The actions of the gray hat hacker helped address a vulnerability in the renowned social network. However, Khalil Shreateh wasn’t accepted into the white hat hacker community because he didn’t adhere to the rules.

Overall, cybersecurity is a battlefield where individuals with different motivations are engaged. Let's explore more examples of such battles.
At what cost does cybersecurity come?
On average, companies allocate 12.7% of their budget to information security. It's significant, but preventing damage from cyberattacks is much cheaper than remediation. According to Gartner, companies are projected to spend $188.3 billion on cybersecurity in 2023, with a forecasted amount of $262 billion by 2026.
Companies pay considerable attention to cybersecurity, as it directly impacts their budget and reputation. But what about governments? Rumors suggest that some countries have a cyber army at their disposal, capable of both defense and offense in the cyber realm.
State cyber armies
There are ongoing discussions regarding certain states creating and maintaining specialized groups or units involved in cyber attacks and hacking activities. These groups are sometimes called "hacker armies" or "cyber forces." The objectives of these state-sponsored groups can vary and may include reconnaissance operations, cyber espionage, attacks on hostile networks, disruption of communications, or cyber sabotage.
However, it's essential to note that information about such activities is typically classified and rarely officially confirmed. The actions of state-sponsored hacker groups are often covert and not always open to public discussion. Additionally, not all states have the capabilities and resources to establish and sustain such groups.
Nevertheless, we are aware of some examples.
The Equation Group
The Equation Group is one of the most sophisticated and advanced cyber armies. This group gained widespread attention after research conducted by Kaspersky Lab in 2015.
The Equation Group is interested in various targets and employs advanced techniques for their cyber attacks. Their activities encompass espionage, cyber infiltration, the deployment of malware, and cyber programming.
A significant aspect of the Equation Group's operations involves the use of a toolkit of vulnerabilities and exploits, including the "Equation Drug," "Equation Group," and "Equation Monkey," enabling them to carry out complex and stealthy attacks. The vulnerabilities exploited by the Equation Group have proven unique and highly effective.
The Equation Group is also known for its ability to infect hard drives and embed itself in computer firmware BIOS chips, making their malware nearly impossible to remove and granting them continued access to compromised systems.
There are suspicions of a connection between the Equation Group and the United States National Security Agency (NSA), although no official confirmation has been provided.
Lazarus Group
We are accustomed to considering North Korea a country with minimal technology. However, surprisingly, one of the most well-known hacking armies is purportedly associated with North Korea. It was first discovered in 2009 and has since attracted significant attention in cybersecurity due to its activity and sophisticated attacks.
The Lazarus Group has shown interest in various targets and sectors, including financial institutions, government organizations, energy companies, and the entertainment industry. Their activities encompass cyber espionage, penetration, theft of economic data, investigations, and sabotage.
One of the most notable and significant actions of the Lazarus Group was the attack on Sony Pictures Entertainment in 2014. The attack caused significant damage to the company and garnered worldwide attention. This group is also suspected of involvement in numerous other cyber attacks, including bank heists, reconnaissance operations, and attacks on cryptocurrency platforms.
Lazarus Group is renowned for its advanced technical capabilities and the utilization of sophisticated malware such as the "WannaCry" and "Code Red" ransomware. They have also employed phishing attacks, social engineering, and vulnerability exploits to achieve their objectives.
Ukrainian Cyber Alliance, UCA
The Ukraine Cyber Alliance isn’t a state structure but consists of enthusiasts. However, this group of hackers can be called a fully-fledged cyber army of the country. The alliance emerged in 2016 during the ongoing cyber war between Russia and Ukraine.
The alliance is known for its numerous successful operations. Since 2024, Ukrainian hacktivists have been countering cyber attacks from Russia. Specifically, they have been repelling many DDoS attacks from hackers such as KillNet and the Russian Cyber Army.

The presence of dedicated cyber armies once again confirms that the digital realm is just as significant as the physical world. To further underscore the importance of cybersecurity, let's discuss the most prominent cyber crimes and their consequences.
Top 3 сybercrimes of the 21st century
There have been numerous cybercrimes committed in the 21st century. However, some of them stand out due to their scale. Let's look at three cases where the data of the most significant number of people were affected.
3rd place: Equifax
Equifax is a renowned United States agency specializing in consumer credit reporting. In 2017, the company faced a massive cyber attack, resulting in 145 million users being affected. Despite receiving detailed instructions, Equifax failed to update its software, which could have protected vulnerable components.
Hackers Wu Zhiyong, Wang Qian, Liu Lei, and Xu Ke utilized malicious software that granted them access to personal data. The consequences have remained unresolved and may never be fully rectified. Customer accounts continue to face threats as long as they exist.
The hackers were identified as representatives of the Chinese armed forces and were charged with computer fraud and economic espionage.
Equifax is obligated to pay $425 million to the affected individuals.
2nd place: Marriott International
Marriott International, Inc. is a hotel company that manages 7400+ properties in 135 countries. The company has suffered from multiple hacking attacks, indicating insufficient cybersecurity measures.
The first data breach at Marriott occurred in 2018 when hackers accessed the reservation database. The company experienced 10 attacks, one of which granted hackers access to customers' payment card information. Fortunately, the card numbers were encrypted.
As a result of the attack, the data of 500 million individuals was compromised. Some experts attribute the breach to Chinese hackers.
Marriott is fined £18.4 million for this breach. However, in 2020, the company was hacked again.
1st place: YAHOO!
Yahoo Worldwide is an American web service provider known to almost everyone. Most people had a Yahoo! email account in the past, which made the company an attractive target for hackers. 2013 the most significant hacking incident occurred, compromising 3 billion accounts! These were all the accounts that existed in the database at that time. Hackers gained access to all users' email accounts.
However, in 2012 Yahoo! had already experienced attacks from hackers. Although there were no data breaches then, the company did not take the attack as a warning. Employees failed to implement adequate cybersecurity measures. It was only in 2017 that the company finally acknowledged the scale of the disaster. Yahoo! paid $50 million in compensation for the damages and committed to providing credit monitoring services to 200 million users for two years.
Final words
It's obvious that the consequences of cyber threats can be catastrophic. Unprecedented cases of financial damage, legal lawsuits, and reputation loss await companies that have neglected user data security.
The experts at Vilmate are always ready to assist you in implementing protection for your website, application, cloud storage, and more. Our cybersecurity professionals utilize reliable encryption methods to safeguard your data. So feel free to contact us anytime if you need help with cyber security. We will help prevent possible negative consequences in the future.




